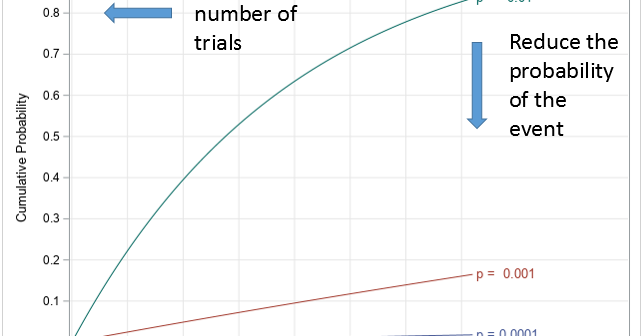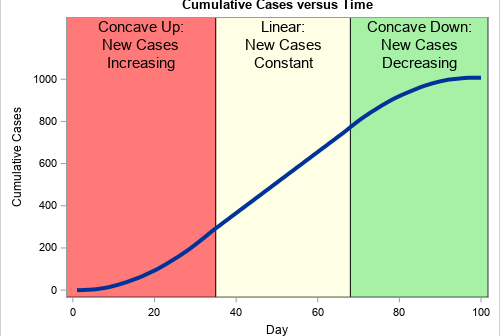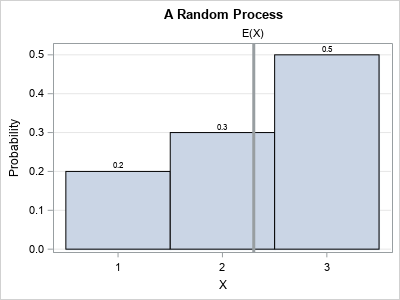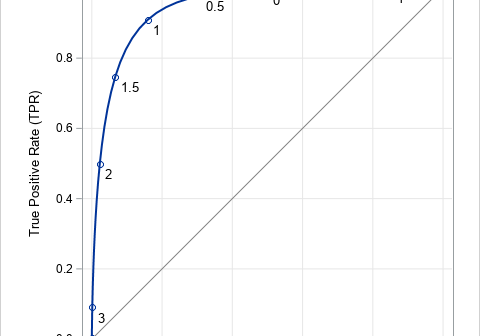
This article uses simulation to demonstrate the fact that any continuous distribution can be transformed into the uniform distribution on (0,1). The function that performs this transformation is a familiar one: it is the cumulative distribution function (CDF). A continuous CDF is defined as an integral, so the transformation is