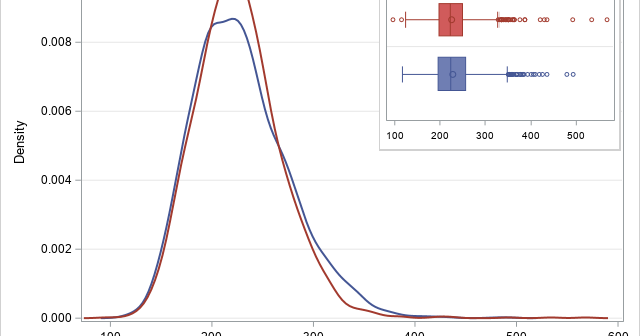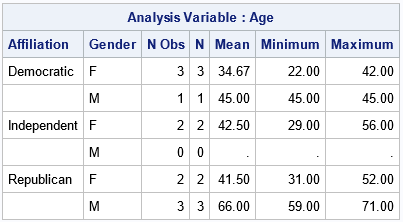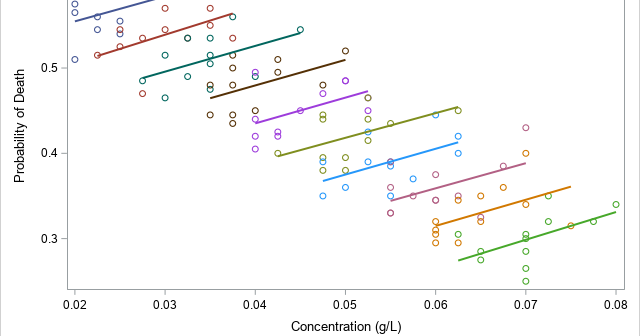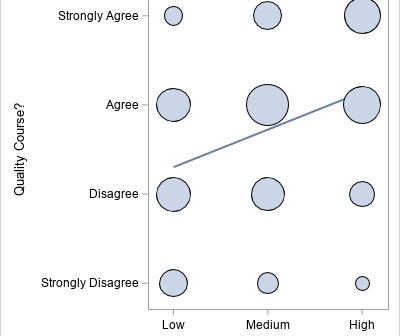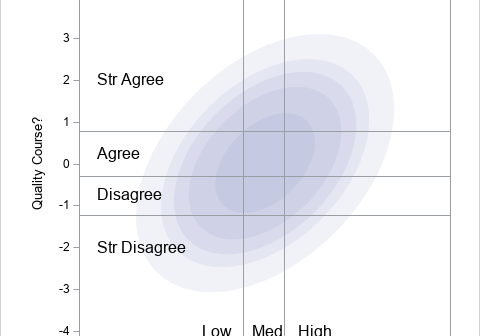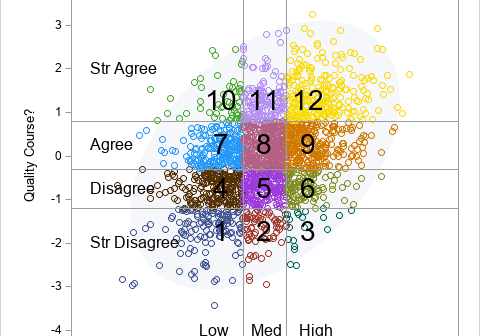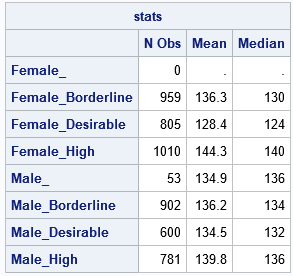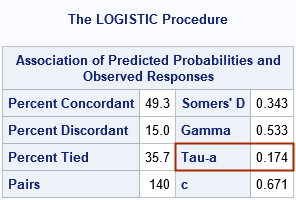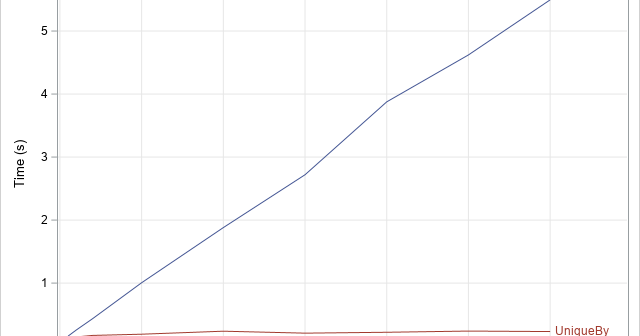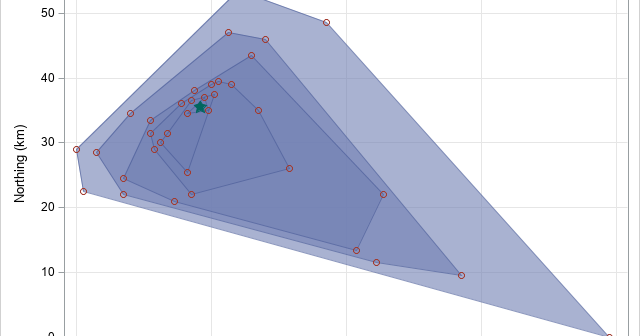
This article looks at a geometric method for estimating the center of a multivariate point cloud. The method is known as convex-hull peeling. In two-dimensions, you can perform convex-hull peeling in SAS 9 by using the CVEXHULL function in SAS IML software. For higher dimensions, you can use the CONVEXHULL