The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs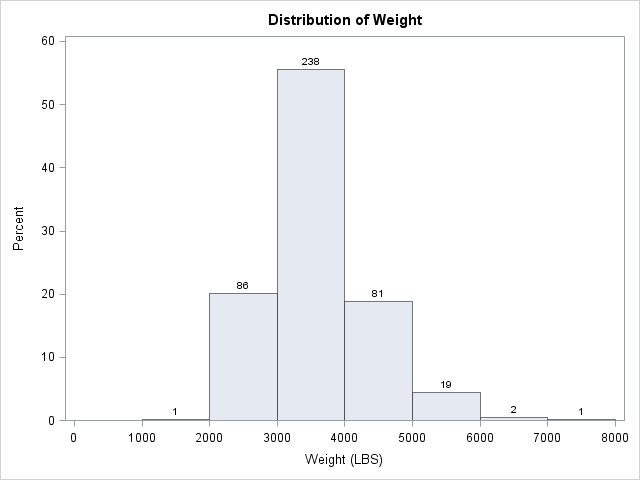
It is often useful to partition observations for a continuous variable into a small number of intervals, called bins. This familiar process occurs every time that you create a histogram, such as the one on the left. In SAS you can create this histogram by calling the UNIVARIATE procedure. Optionally,
Are you still using the old RANUNI, RANNOR, RANBIN, and other "RANXXX" functions to generate random numbers in SAS? If so, here are six reasons why you should switch from these older (1970s) algorithms to the newer (late 1990s) Mersenne-Twister algorithm, which is implemented in the RAND function. The newer
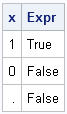
Every programming language has an IF-THEN statement that branches according to whether a Boolean expression is true or false. In SAS, the IF-THEN (or IF-THEN/ELSE) statement evaluates an expression and braches according to whether the expression is nonzero (true) or zero (false). The basic syntax is if numeric-expression then do-computation;
