The popularity of collagen supplements has exploded over the last few years. As with most things, the benefits tend to get blown out of proportion on the internet. However, there might be some benefit to taking a collagen supplement. Let’s dig down into the science and see if it might be worth it.
Are #collagen supplements worth it? What can they help with? #saslife Click To TweetWhat is collagen?
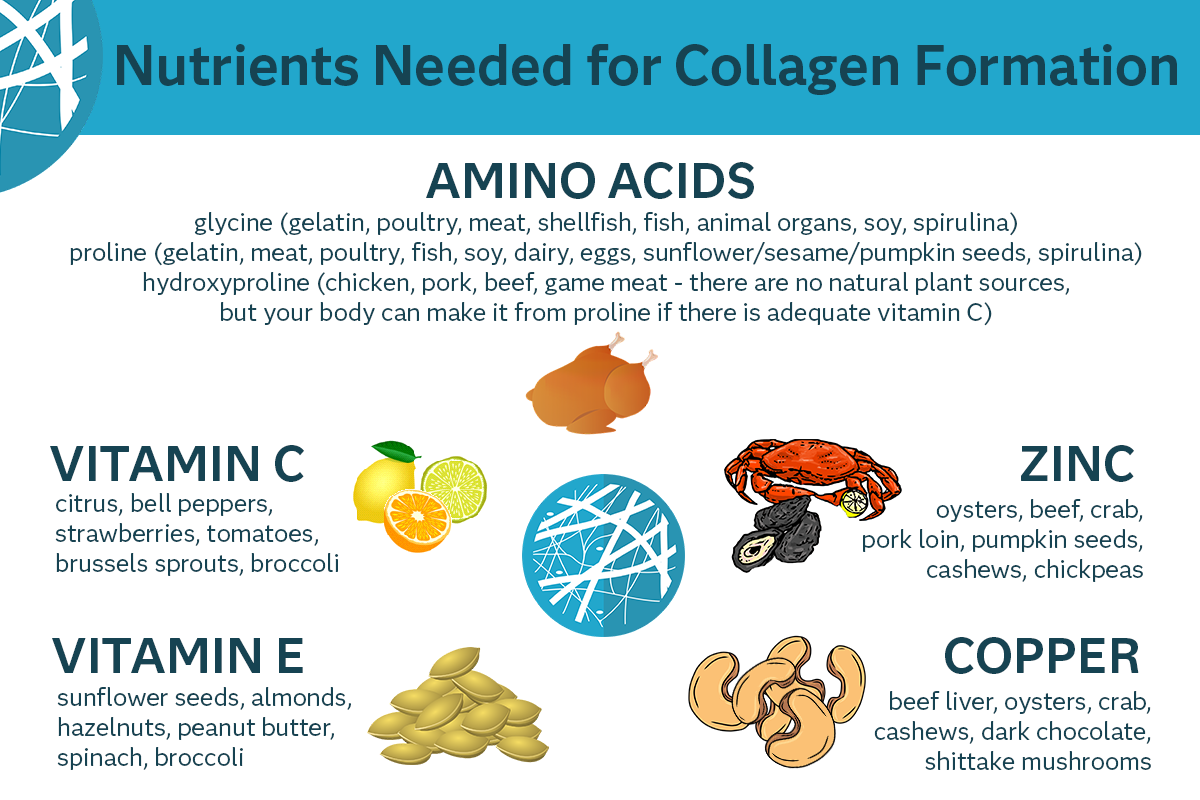
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body and is essential to maintaining healthy connective tissue in skin, bone, cartilage, tendons, muscles and blood vessels. There are actually 28 different types of collagen, but the most common types are types I - IV, with type I comprising over 90% of the collagen in our bodies. Since collagen is a protein, it is made up of amino acids (the building blocks of protein), with glycine, proline and hydroxyproline being the 3 most abundant amino acids.
Collagen acts like the glue that holds us together. It has several roles in the body, including providing elasticity and strength to our skin, repairing and replacing skin cells, and maintaining the health of joints, bones, ligaments, tendons, hair, skin and nails.
Our bodies gradually make less collagen as we age, but production drops even quicker if we smoke, drink too much alcohol, have too much sun exposure or don’t get enough sleep or exercise. Chronic stress, or elevated cortisol levels, can also reduce collagen production.
Dietary collagen can only be obtained from animal sources. There are nutrients that can help boost our body’s natural formation of collagen though, like vitamin C, zinc, copper and certain phytonutrients like anthocyanins.
Collagen Supplements
Collagen supplements are derived from animal sources, like beef, chicken or even fish. As with other protein sources, most of the collagen you eat is broken down into individual amino acids during digestion. There is some evidence that some collagen peptides may remain intact as they are absorbed.
Most collagen supplements are typically hydrolyzed, meaning they are already broken down into amino acids and or chains of amino acids (peptides). This can help to improve absorption and make it easy to mix into cold liquids. The specific composition of these “collagen hydrolysate” or “collagen peptide” products can vary somewhat depending on how they are processed, which typically involves heat and enzymes. Gelatin also contains collagen, but it is only partially hydrolyzed, so it is not soluble in cold water.
Benefits of Collagen Supplements
Most research around collagen shows benefits for skin and joint health, but there are other areas that show some positive results as well.
Skin
Many studies have found that supplementing with collagen can reduce the signs of aging. A 2021 review and meta-analysis found that supplementing with hydrolyzed collagen reduced wrinkles and improved skin hydration and elasticity. It has also been found to significantly improve wound healing.
Joints
A meta-analysis from 2023 concluded that supplementation of collagen (specifically type II) can improve joint pain and/or flexibility in osteoarthritis.
Bones
There are also some smaller studies that suggest supplementing with collagen can help with bone health and hair and nail growth.
Gut
In theory, collagen supplements could play an important role in maintaining a healthy connective tissue throughout our digestive tract. There is some evidence that collagen supplements may protect against intestinal permeability (leaky gut) and help maintain intestinal barrier function.
Sleep
Glycine, the main amino acid found in collagen, also acts as a neurotransmitter. In studies, glycine has been shown to improve sleep quality and shorten the time it takes to fall asleep.
How to Choose and Use Collagen Supplements
There are all kinds of collagen supplements on the market these days. Most studies have used doses ranging from 2.5g to 15g per day so for a consistent intake of collagen, supplements can be helpful. Look for hydrolyzed collagen, from a reputable company, meaning they have at least GMP certifications and preferably testing from a 3rd party lab. A few of my favorites are Great Lakes Wellness and Vital Proteins. Most collagen powders can easily disappear into drinks or smoothies.
You can also get collagen naturally from foods including:
- Tough cuts of beef like pot roast and brisket.
- Skin and bones from fish.
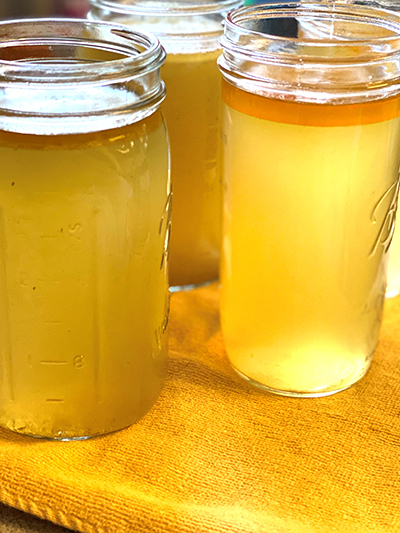
- Bone broth or any soups either made from bone broth or slow cooked with bones (amount will vary depending on the types of bones used and how long it was cooked).
Bone Broth
Makes ~10 cups
PRINT RECIPE
Ingredients
About 2 lbs. of bones: leftover from meals, from a whole baked chicken, etc. (make sure to include chicken feet or beef knuckles for higher collagen content)
8 cups cold water - enough to cover the bones and come to 1-inch below MAX fill line
1-2 Tbsp apple cider vinegar
2 tsp-1 Tbsp sea salt
Flavor options:
1 medium onion peeled and quartered
2-3 cloves garlic peeled and sliced in half or crushed
1 tsp turmeric powder or 1 inch piece of fresh chopped turmeric
1-2 inch piece of fresh ginger root
1 Tbsp dried oregano, thyme or rosemary
1 Tbsp whole peppercorns
Directions
Pressure Cooker
- Combine all ingredients in the pressure cooker
- Fill water to about 2 inches above bones or just below the MAX line in your pressure cooker
- Set on low pressure for 120 minutes and let the pressure release naturally
Slow Cooker
- Combine all ingredients in your slow cooker
- Fill water to about 2 inches above bones or just below the MAX line
- Set on low (if that’s an option) and cook for 12 hours
Stove Top
- Combine all ingredients in large stock pot
- Fill with water to 4 inches above bones
- Bring to boil, cover, reduce heat and simmer at least 12 hours
- You can skim off any foam that accumulates on top as needed
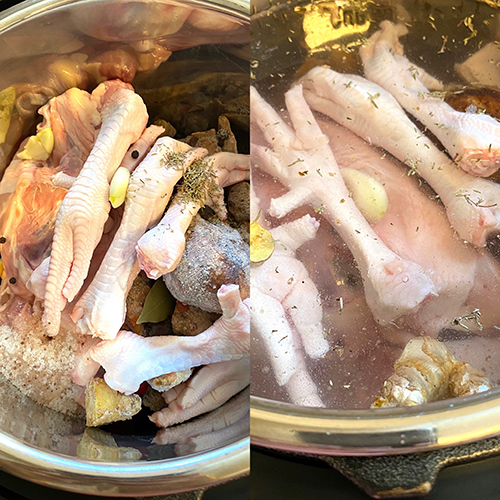

All methods
- Let the broth cool then strain into glass canning jars
- Discard the bones and vegetables
- You can easily skim the fat off the top once refrigerated to avoid an overly greasy broth
Notes
- Broth may be frozen for months or kept in the refrigerator for about 5 days.
- Broth can sipped as a warm drink (remember it contains protein and electrolytes), or it can be used in soups, stews, braised dishes or sauces.
- You can also use it to cook grains to up their nutritional value.