The supplement industry is booming. In just the US alone, it’s estimated that there are over 100,000 different products sold, with the overall market nearing $70 billion in sales!!! Globally, this figure rises to about $180 billion (in 2024) and is projected to reach over $250 billion by 2029.
The loosely regulated supplement industry can be very confusing, as companies can seemingly say whatever they want in their marketing. They don’t even have to test products (for anything) before putting them on the market.
Supplement companies do not need FDA approval for safety or effectiveness before their products are sold to the public.
Many of the supplements you see online or even in stores might not be what they claim to be. Some are mislabeled, contaminated, or completely missing key ingredients. But this doesn’t mean that all supplements are poor quality. Here are some guidelines to help you choose high-quality brands.
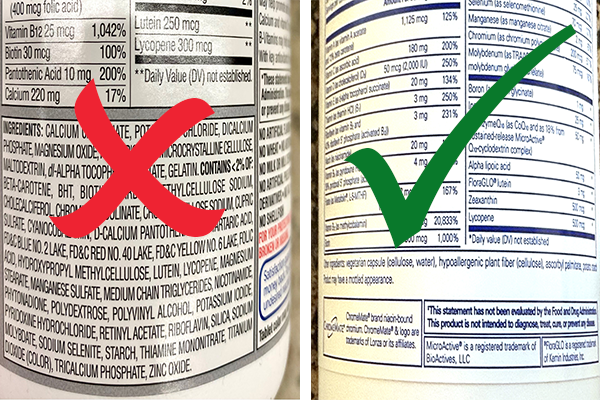
- Read the “other ingredients.” Just below the Supplement Facts you will see all the other things that are in the supplement. Choose ones that don’t have unnecessary fillers, binders, coatings or other additives – like artificial colors and titanium dioxide.
- Check for 3rd party testing for purity and potency. Reputable brands invest in 3rd party testing. These independent labs test what is in the supplements to make sure they meet label claims and don’t contain contaminants. Look for supplements with USP, NSF or at least GMP seals:
- GMP – Good Manufacturing Practices help to ensure facilities are clean, equipment is working, and workers are trained to prevent contamination and ensure consistency. This is the bare minimum to ensure quality during manufacturing and does not include end product testing.
- USP – U.S. Pharmacopeia evaluates for identity, potency, purity and performance, meaning what is on the label is in the product, it is free of contaminants, and it actually breaks down or dissolves after you swallow it so it can be absorbed. This seal includes GMP.
- NSF – The National Sanitation Foundation grants its seal of approval to products that meet purity standards. They evaluate products for unacceptable levels of contaminants like heavy metals, pesticides and herbicides. This seal includes GMP. They also certify sport safe supplements for competitive athletes as part of their NSF Certified for Sport certification.
- ConsumerLab.com – This independent company purchases supplements from stores and tests them similar to USP (for identity, potency, purity and disintegration). They also provide education about that product like what it is, what it does, concerns, cautions and recalls. You have to pay to see their product reviews, but they are very thorough and easy to understand.
- Avoid “proprietary blends.” Some supplements hide behind proprietary blends, which group ingredients together without specifying individual ingredient dosages. This lack of transparency makes it impossible to know what you’re consuming. Opt for products with clearly listed ingredient amounts.
- Transparency is a must. Trustworthy brands are transparent about their sourcing, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. You should be able to easily access information about where the ingredients come from, how they are processed, and what steps are taken to prevent contamination. Reputable brands share their research and manufacturing practices.
Other things to consider
Know the active ingredients and the appropriate form and dose. This is a little tricker and where speaking with a registered dietitian or other informed health care provider can be helpful.
To benefit from certain supplements, you need the right dose, and it needs to be in the right form. For example, if you are looking to take magnesium to help with constipation, you would want to make sure you choose magnesium citrate, not magnesium glycinate. You would also need to take enough for it work as an osmotic laxative – for most, this is around 300mg. If you took 100mg of magnesium glycinate this would likely NOT help with your constipation.
A few high-quality brands that I trust include:
Purchasing Quality Supplements
Now that you know how to find a quality brand, where should you purchase that product? This is an important question, as counterfeit supplements are more common than you might think.
Thousands of counterfeit supplements are sold online, with estimates suggesting that between 10% and 60% of products sold on certain third-party retailers are fake. One study found that 57% of 30 specific immune-supporting supplements bought on Amazon were counterfeit.
Some supplement companies are now warning consumers not to buy their products from third-party resellers due to the high incidence of counterfeits. Counterfeits aren’t just useless; they can be dangerous. Some of these counterfeit supplements have been found to contain dangerous substances like heavy metals, pharmaceuticals or allergens.
How to Avoid Counterfeit Supplements
- Buy from trusted sources (official brand website or trusted retailers like Pure Formulas and Vitacost). Avoid buying supplements from unknown sellers or sketchy websites. Counterfeit supplements are also sold through third-party sellers (Amazon, Walmart, eBay, Alibaba, etc.), especially on less regulated websites.
- Don’t fall for prices that are “too good to be true.” Scam supplements can sometimes come with unusually low prices (compared to trusted retailers). Compare prices across reputable websites to get an idea of what’s “normal” for that product.
- If you do order the product online, pay attention to the bottle and contents. Sometimes counterfeit supplements come with wonky labels – the print might be crooked, the font might be off, or they may not have batch numbers or expiration dates either. Also make sure the safety seals are intact. If the supplement smells different than it had before or looks discolored or the capsules are hard, this can indicate poor handling/storage or a counterfeit product. This is a little harder to discern if you have never purchased the product before.
Hopefully this guide simplifies the process of choosing quality supplements by offering tips on reading ingredient labels, identifying reputable brands, and spotting potential red flags. Follow the guidelines outlined above to make informed decisions and select safe, effective supplements.
Before starting any new supplement regimen, consult with a knowledgeable healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
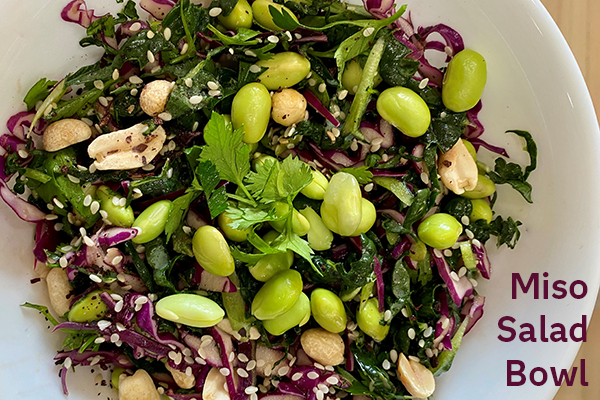
Miso Salad Bowl
Makes 4 servings
Recipe adapted from: Cooking for Peanuts
PRINT RECIPE
Ingredients
Salad
1 large bunch of kale (about 4 packed cups)
½ medium red cabbage (about 4 packed cups)
10 oz shelled frozen edamame (cooked using package instructions)
1 Tbsp olive oil
¾ tsp sumac (optional)
3 scallions, thinly sliced (white and light green parts)
½ cup chopped cilantro or parsley, mint, or basil
1 Tbsp sesame seeds
½ cup unsalted peanuts, roughly chopped (optional)
Miso Sauce
1 ½ Tbsp white miso or mellow miso
1 Tbsp tamari or soy sauce
3 Tbsp rice vinegar
2 cloves garlic, minced
1 ½ inches ginger, minced or grated
1 Tbsp maple syrup
Instructions
- Chop kale and cabbage in a food processor until finely chopped. Transfer them to a large bowl. Add in olive oil, cooked edamame, sumac, scallions, herbs, sesame seeds and peanuts and mix well.
- Add miso, tamari, vinegar, garlic, ginger, and maple syrup to a jar with a lid. Cover and shake vigorously or whisk the ingredients in a medium bowl.
- Add about half of the dressing to the salad, mix well and let the salad marinate in the dressing for at least 10-20 minutes before serving. Taste again before serving and add more dressing if needed.
Notes
Alternately you can serve this as a cooked salad:
- Place shredded kale and cabbage in a large skillet with olive oil.
- Sauté until slightly wilted.
- Add the edamame and miso sauce, cook until tender, then add the rest of the ingredients when serving.