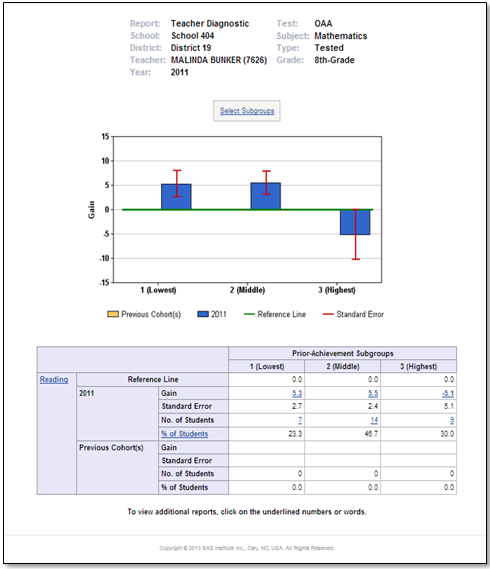
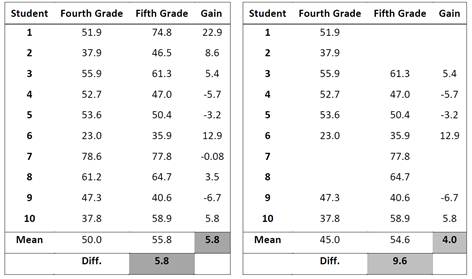
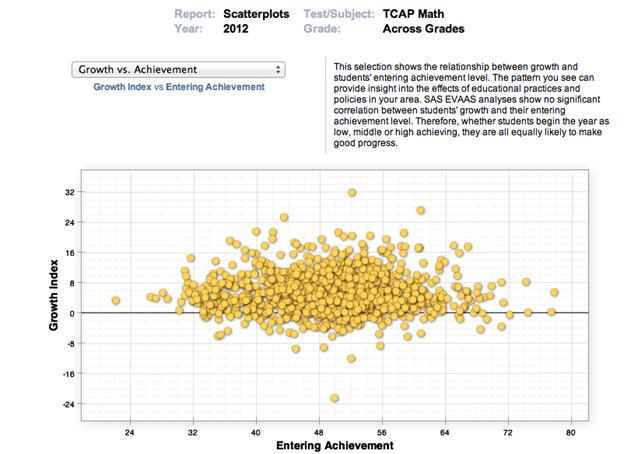
Improving teacher effectiveness is no simple task. Whether a part of a formal evaluation system or for formative feedback, looking at student growth data can be a valuable part of the development process for teachers and administrators. Lubbock Independent School District (Lubbock ISD) uses SAS® EVAAS to improve teaching and