SAS Grid Manager for Platform, SAS Grid Manager, and SAS Viya Workload Management all manage and balance job loads, right? So, are there three SAS products providing the same functionality? Let’s explore, as I am curious in your answer after you read this article.
Each of the three applications has a Graphical User Interface (GUI), which provides basic functionality like monitoring and managing jobs, queues, and hosts. The GUIs differ slightly between applications, but let’s save that detailed conversation for another post. For now, let’s take a look at the applications.
Interfaces
SAS Grid Manager for Platform
SAS Grid Manager for Platform is developed by IBM and provided as an OEM license through SAS. This product was first made available in SAS 9.4 M2. The GUI has matured over time and Figure 1 represents the latest iteration.

SAS Grid Manager for Platform takes advantage of the Load Sharing Facility (LSF), Process Manager (PM), and Platform Web Services (PWS) features. Together these features provide services for job execution, job scheduling and host information. You launch the GUI for SAS Grid Manager for Platform from a separate URL and it is also listed in the Instructions.html file generated during the install process. Most SAS customers use Platform Suite for SAS. It is our legacy product.
SAS Grid Manager
In SAS 9.4 M6, SAS released SAS Grid Manager which balances workloads, supports high availability, and has multiprocessing capabilities. See Figure 2 for a detailed view.

The Balance Workload feature ensures the spread of resources across machines and they are not overloaded with running jobs. High Availability ensures resource availability in case of machine failure and insures jobs still run and execute. Multiprocessing capabilities breaks down jobs, so they run across machines.
The GUI for SAS Grid Manager goes by the name SAS Workload Orchestrator (SWO). You launch the SWO from a separate URL and it is also listed in the Instructions.html, which generates during the install of SAS. Since it is built with the SAS threaded kernel, SAS Grid Manager takes great advantages of the SAS features and capabilities.
SAS Viya Workload Management
SAS developed the SAS Viya Workload Management for the newest version of SAS Viya. The GUI for SAS Viya Workload Management goes by the name Workload Orchestrator (hmmm, sound familiar? 😉). The plug-in appears as a menu item in the left-hand navigation pane from SAS Environment Manager, as seen in Figure 3 below.
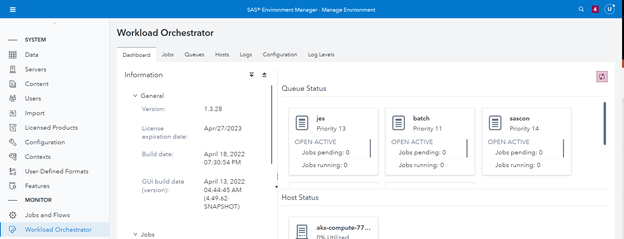
SAS Viya is now cloud native and relies on Kubernetes and its capabilities for balancing job workloads. The SAS Viya Workload Orchestrator is designed to enhance Kubernetes’ workload proficiencies by adding prioritization for jobs, queue management, etc.
Functionality
Now that we've seen some of the differences in the user interfaces, let’s take a look at functionality.
SAS Grid Manager for Platform
SAS Grid Manager for Platform has a Grid Controller and Nodes. As seen in Diagram 1, the SAS Grid Controller machine has Process Manager installed on the machine.
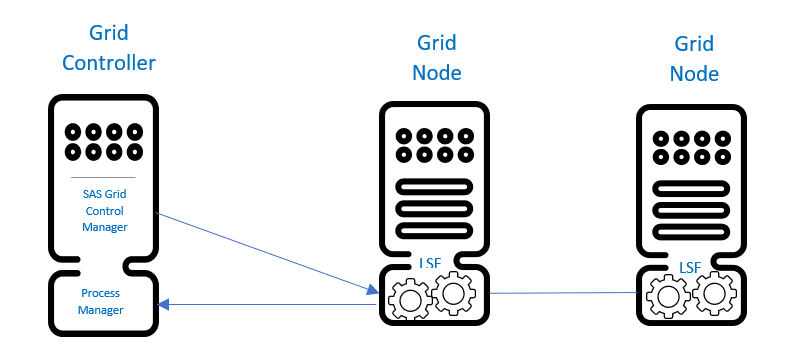
The Process Manager schedules the job and gives the job to the Load Sharing Facility (LSF). LSF executes the job and then submits the results back to Process Manager.
SAS Grid Manager
The SAS Workload Orchestrator (SWO) is the “brains” that acts as a coordination engine for SAS Grid Manager. As depicted in Diagram 2, the SWO keeps track of all of the entry points for jobs, including jobs that come in through the Metadata Server (e.g., Enterprise Guide sessions), Mid-Tier (e.g., BI Server sessions), and through batch submission (e.g., usage of gsub utility).
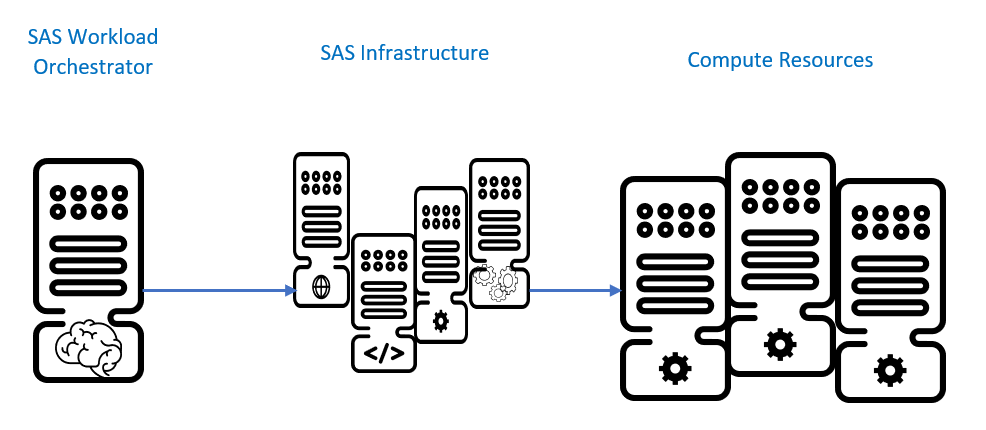
These entry points then utilize compute resources; those resources may be managed through the Workspace Server, Stored Process server, or may be spawned directly through batch submission.
SAS Viya Workload Management
SAS Viya Workload Management extends the Kubernetes capabilities. SAS Compute talks to the Launcher Service, followed by the Workload Orchestrator Manager, which talks to the Workload Orchestrator Server. This flow is depicted in Diagram 3 below.
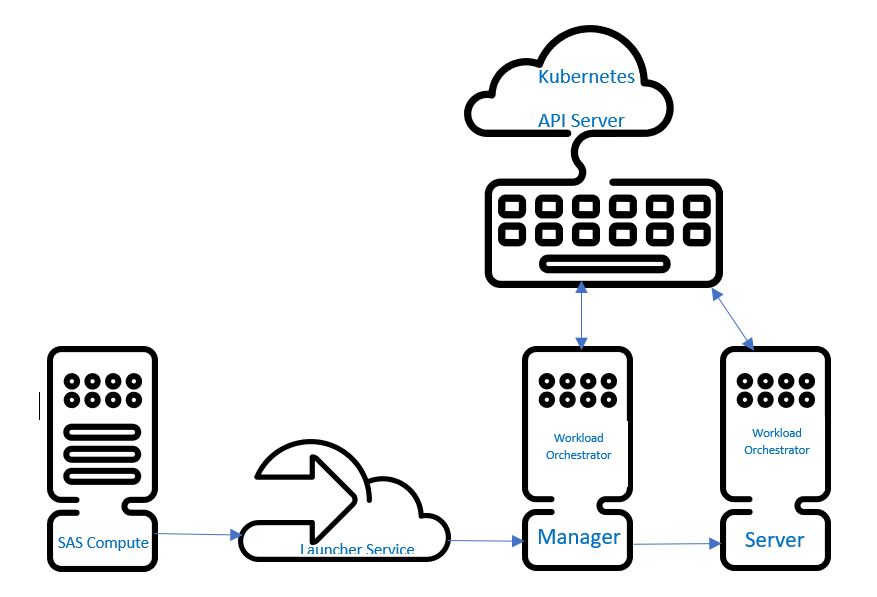
The Kubernetes API Server talks to the Workload Orchestrator Manager and Server. It determines which nodes can start a pod for jobs. SAS Viya Workload Management adds queue prioritization and other features as well.
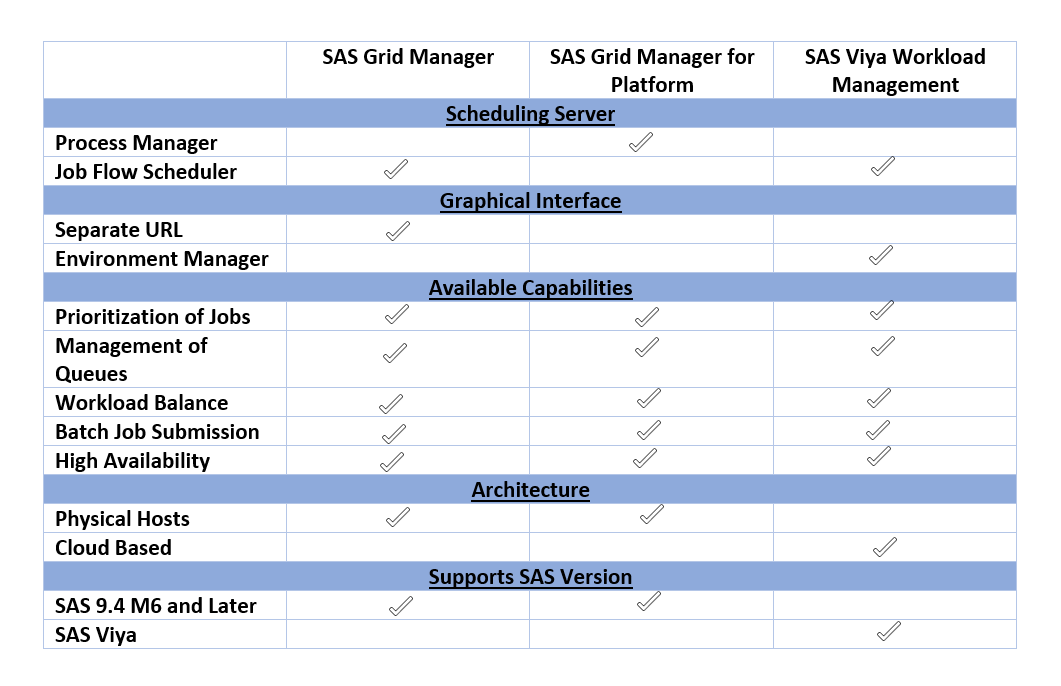
Side-by-side comparison
The following table summarizes the features of each product we’ve discussed in this article.
Finally
So, what do you think? Are SAS Grid Manager, SAS Grid for Platform and SAS Viya Workload Management alike or different? Can we agree on both? In my opinion, there are distant differences but there are some similarities, also..:-)
To summarize, all three products manage jobs and processes. SAS Grid Manager and SAS Grid Manager for Platform are similar running on physical hardware in the older version of SAS with multiple applications to manage. While SAS Viya Workload Management is running on the newest release of SAS in a cloud-based environment taking advantage of the Kubernetes technology in a one stop shop of SAS Environment Manager.

2 Comments
Nice job Ursula!
Thank you so much!