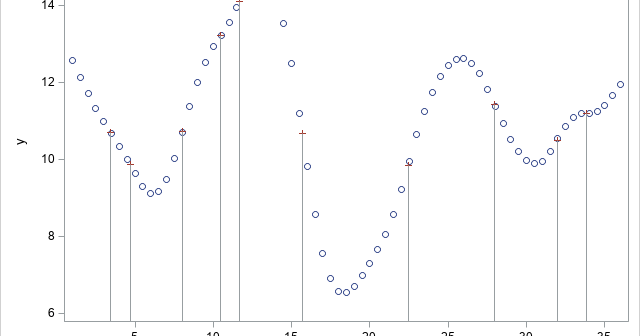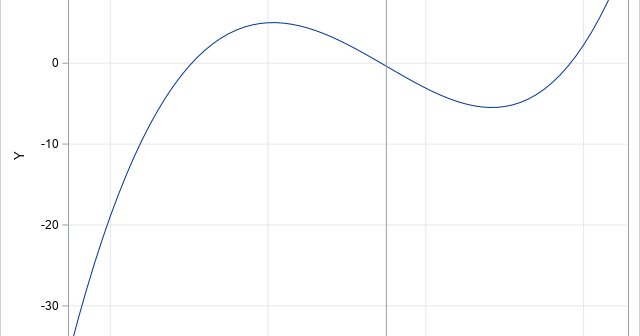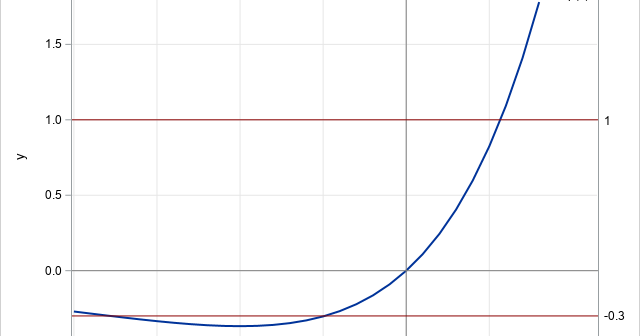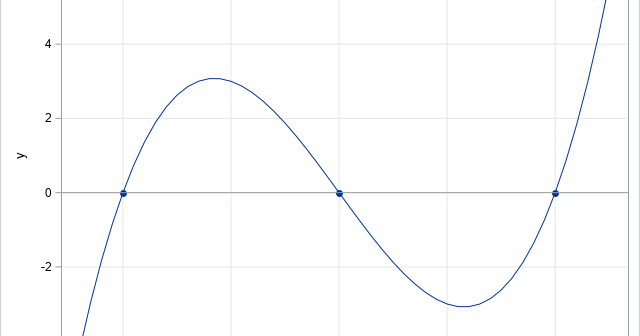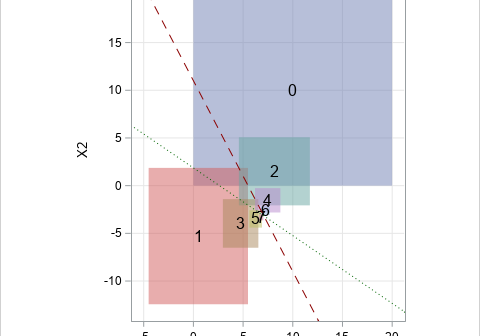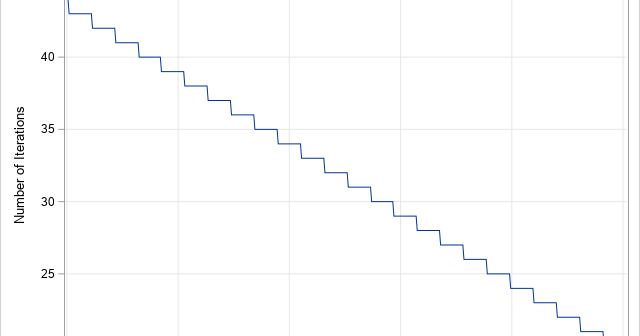
Newton's method was in the news this week. Not the well-known linear method for finding roots, but a more complicated method for finding minima, sometimes called the method of successive parabolic approximations. Newton's parabolic method was recently improved by modern researchers who extended the method to use higher-dimensional polynomials. The