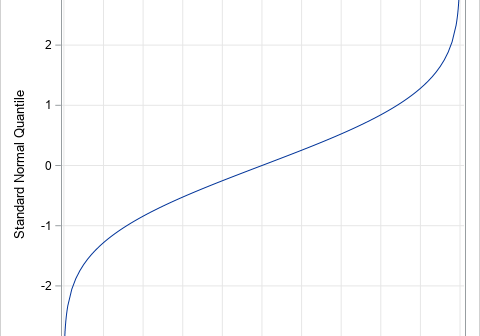
Monotonic transformations occur frequently in math and statistics. Analysts use monotonic transformations to transform variable values, with Tukey's ladder of transformations and the Box-Cox transformations being familiar examples. Monotonic distributions figure prominently in probability theory because the cumulative distribution is a monotonic increasing function. For a continuous distribution that is