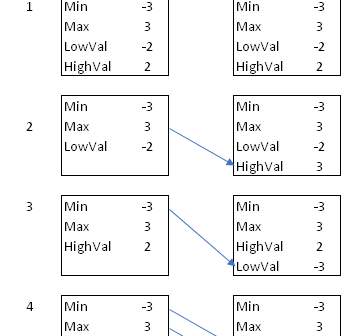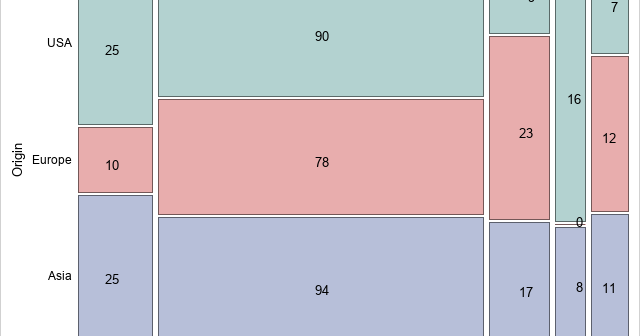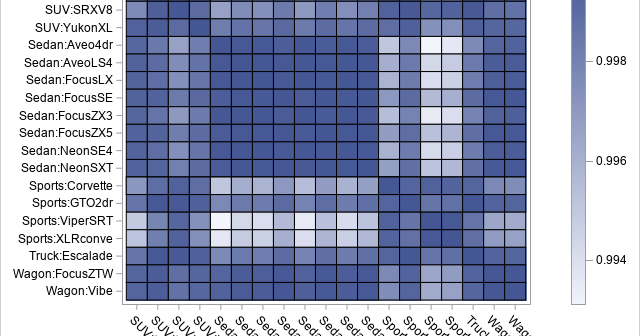
An important application of the dot product (inner product) of two vectors is to determine the angle between the vectors. If u and v are two vectors, then cos(θ) = (u ⋅ v) / (|u| |v|) You could apply the inverse cosine function if you wanted to find θ in