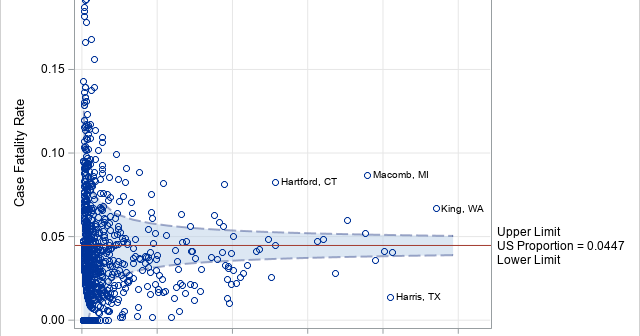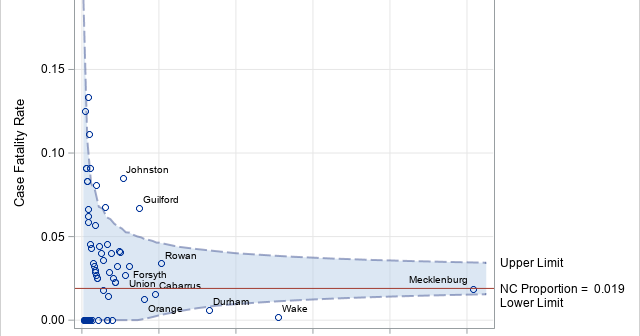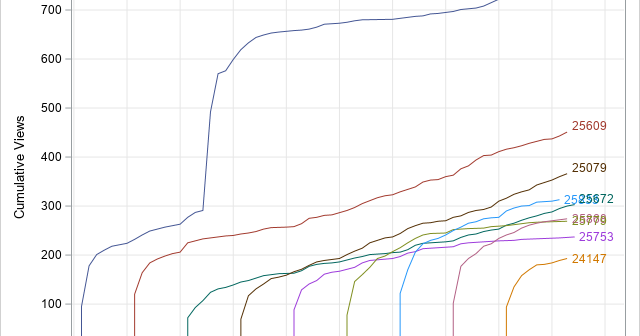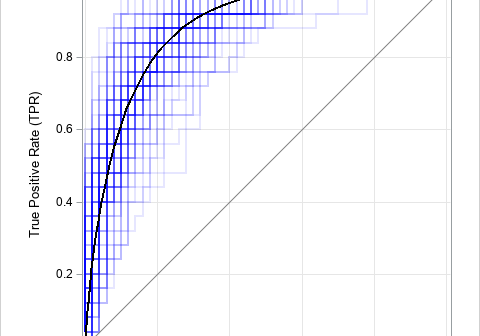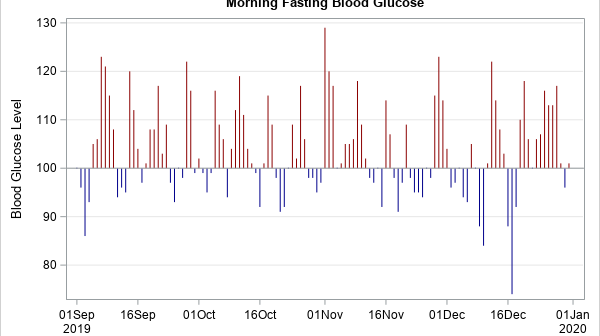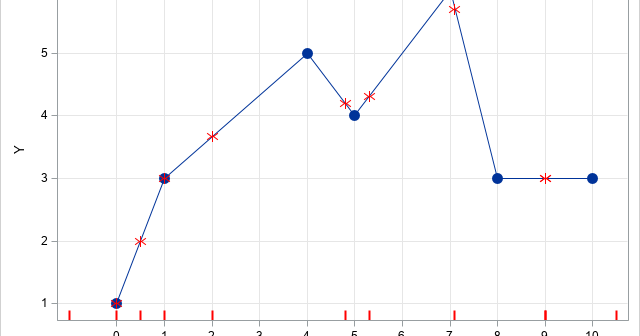
SAS programmers sometimes ask about ways to perform one-dimensional linear interpolation in SAS. This article shows three ways to perform linear interpolation in SAS: PROC IML (in SAS/IML software), PROC EXPAND (in SAS/ETS software), and PROC TRANSREG (in SAS/STAT software). Of these, PROC IML Is the simplest to use and