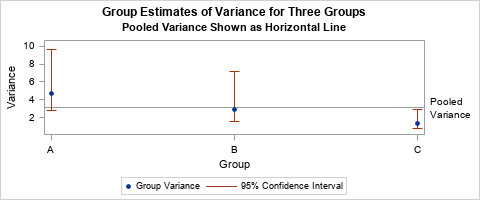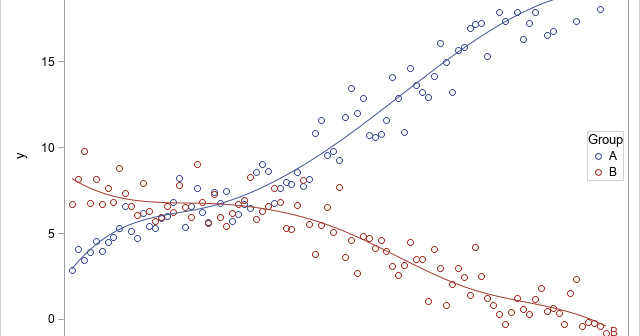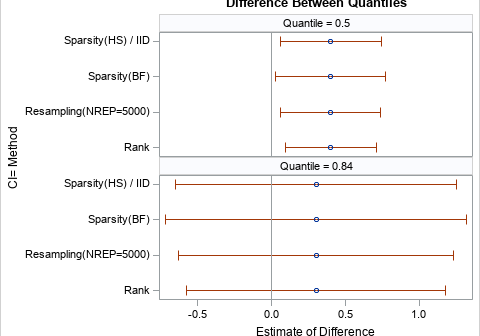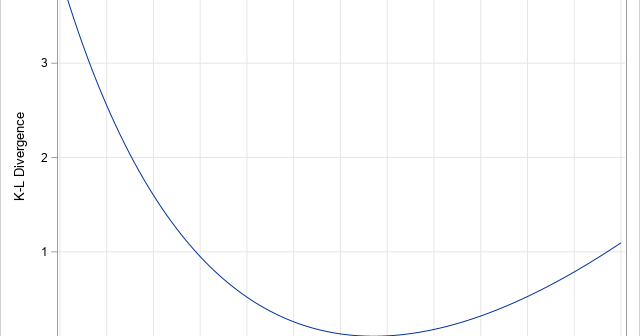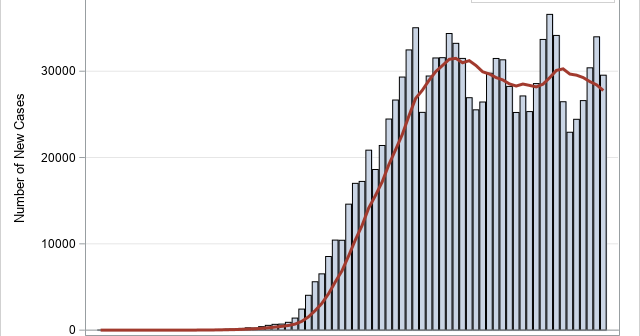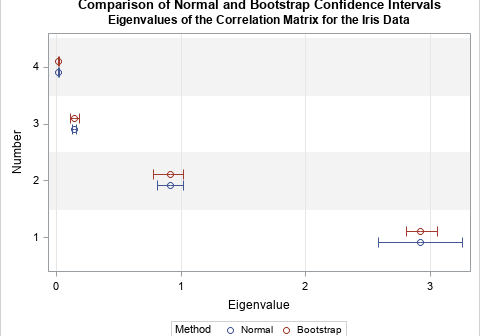
A fundamental principle of data analysis is that a statistic is an estimate of a parameter for the population. A statistic is calculated from a random sample. This leads to uncertainty in the estimate: a different random sample would have produced a different statistic. To quantify the uncertainty, SAS procedures