The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs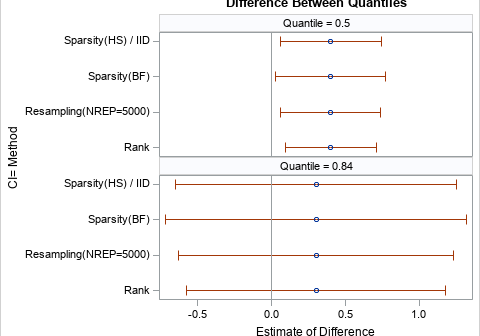
I recently read an article that describes ways to compute confidence intervals for the difference in a percentile between two groups. In Eaton, Moore, and MacKenzie (2019), the authors describe a problem in hydrology. The data are the sizes of pebbles (grains) in rivers at two different sites. The authors
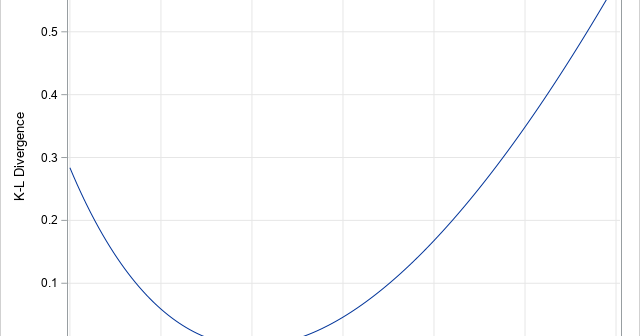
In a previous article, I discussed the definition of the Kullback-Leibler (K-L) divergence between two discrete probability distributions. For completeness, this article shows how to compute the Kullback-Leibler divergence between two continuous distributions. When f and g are discrete distributions, the K-L divergence is the sum of f(x)*log(f(x)/g(x)) over all
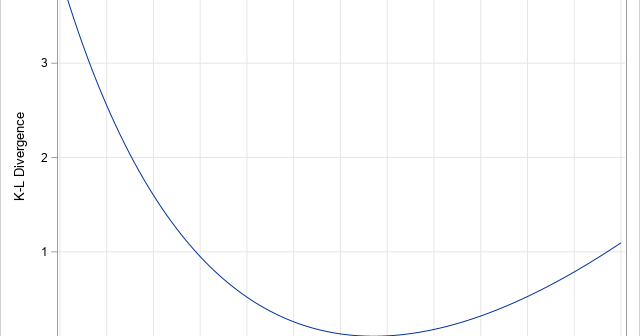
The Kullback–Leibler divergence is a measure of dissimilarity between two probability distributions. An application in machine learning is to measure how distributions in a parametric family differ from a data distribution. This article shows that if you minimize the Kullback–Leibler divergence over a set of parameters, you can find a
