Getting Started with Job Scheduling in SAS Viya
If you have ever had to manually trigger Viya jobs, you know the drill: it is tedious, and one forgotten click can throw everything off.
That is where SAS Viya job scheduling comes in. It lets you automate your programs, data loads, reports, and analytics workflows so they run exactly when you need them, no babysitting required.
What is a Job in Viya?
Think of a job as any piece of SAS work you want to run, such as a program, a data plan, or even a Visual Analytics report refresh. Once it is saved in Viya (for example, from SAS Studio or Data Studio), you can schedule it to run automatically at a set time or on a recurring basis.
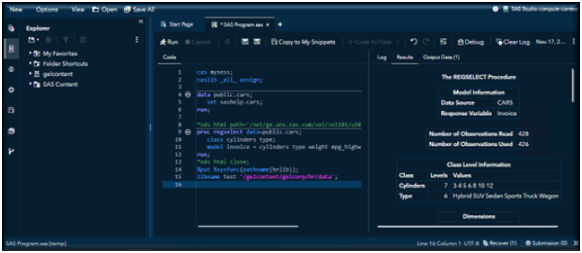
The first step is to write your code. In this example, I am using SAS Studio to create SAS code that will be submitted to Viya CAS for execution.
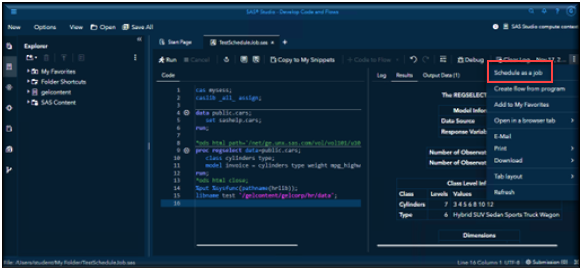
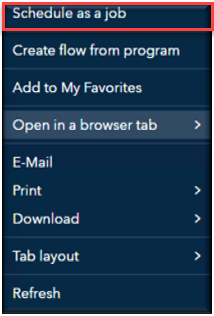
After saving your job in your Viya content folder, open the More menu (the three-dot icon). From the list of options, select Schedule as a Job to create a scheduled job from your code.
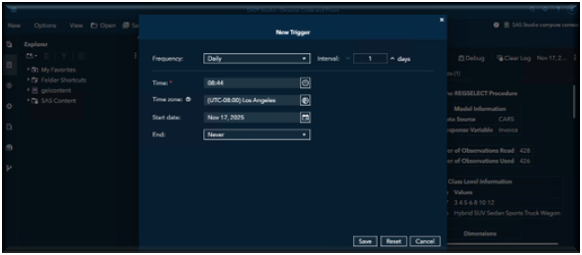
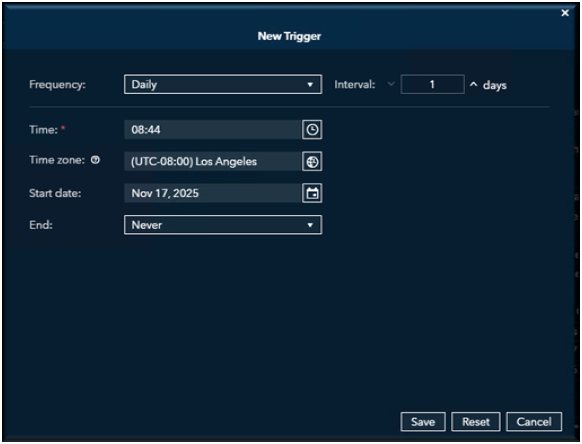
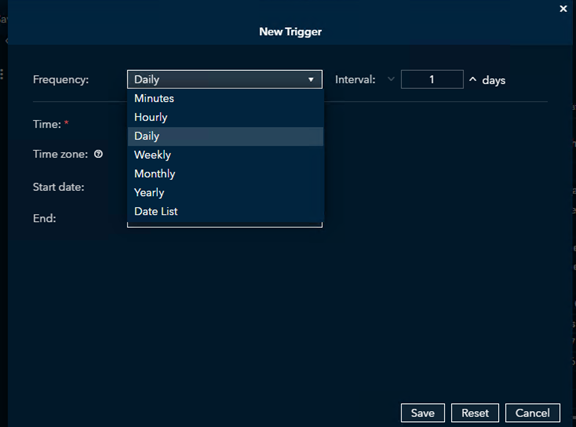
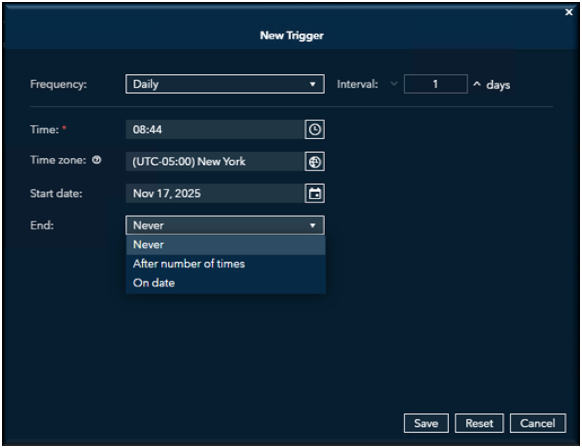
After selecting Schedule as a Job, the New Trigger dialog box appears. From this dialog, choose the Frequency (how often the job should run) and the Interval (how often that frequency occurs).
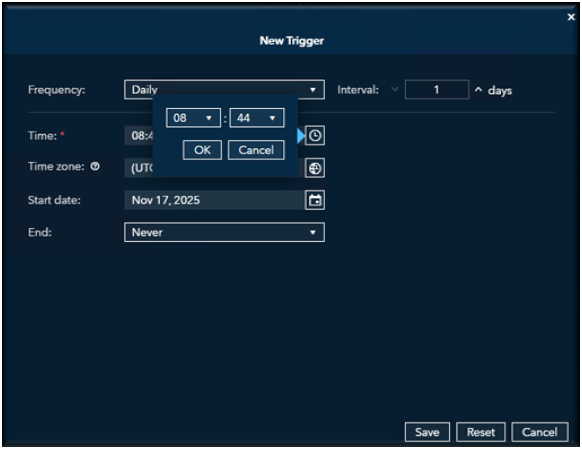
Next, specify the Start Time for when you want the job to begin running.
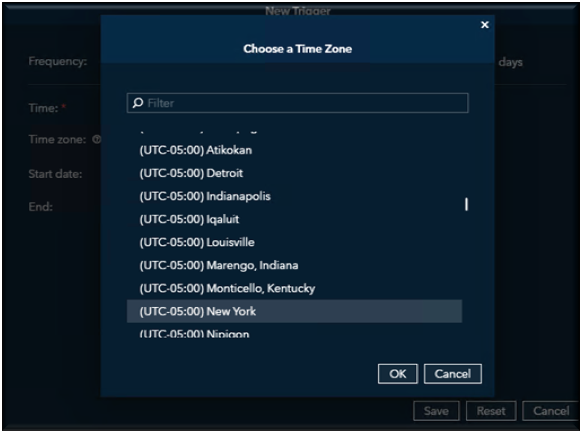
Select the appropriate Time Zone.
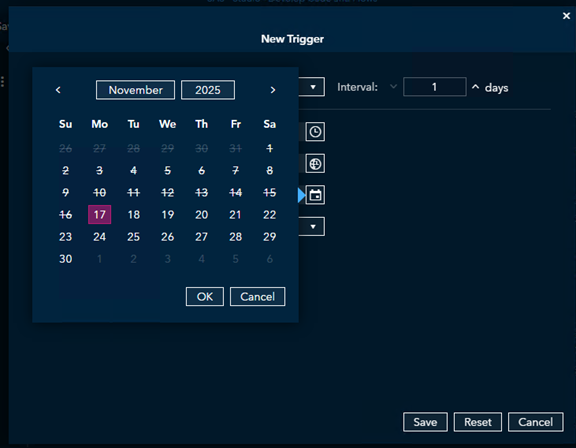
Then, set the Start Date for when the schedule should take effect.
Finally, choose an End Date to define how long the job should remain scheduled.
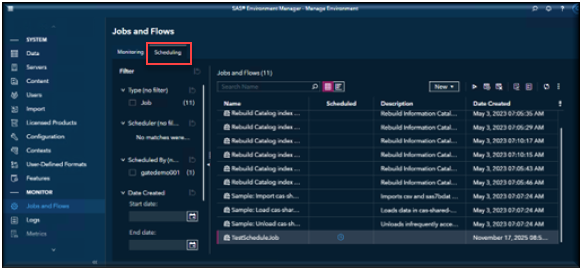
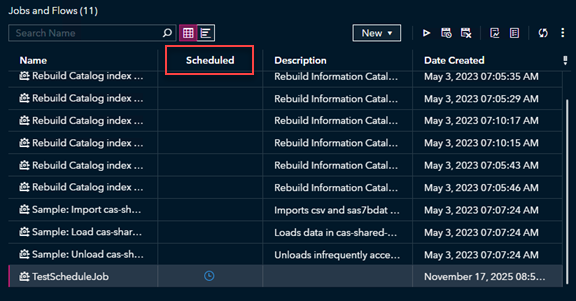
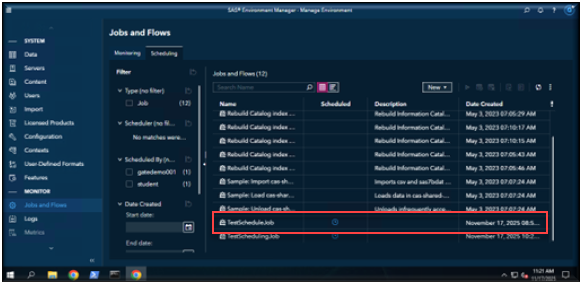
To verify that your job has completed, open Environment Manager and navigate to the Jobs and Flows page. You should see your job listed there, and under the Scheduled column, a blue clock icon indicates that the job has an active schedule.
Scheduling Made Simple
SAS Viya’s Scheduling page (inside Environment Manager) is your main hub for automating jobs. From here, you can run a job immediately, set it to run daily, weekly, or yearly, and manage existing schedules — view, edit, disable, or delete them. You can even run a job as a different user (if you are an admin), which is handy when jobs need specific credentials. Currently, the only trigger type is time-based, so it is all about scheduling by the clock.
Environment Manager is also where you will need to go to edit any jobs you have scheduled using visual tools (Visual Analytics, Visual Statistics, Visual Data Mining and Machine learning, Visual Forecasting and SAS Studio).
The first step is to create a job from the SAS Code/Program you want to automate. Below are the steps to create a job in Environment Manager
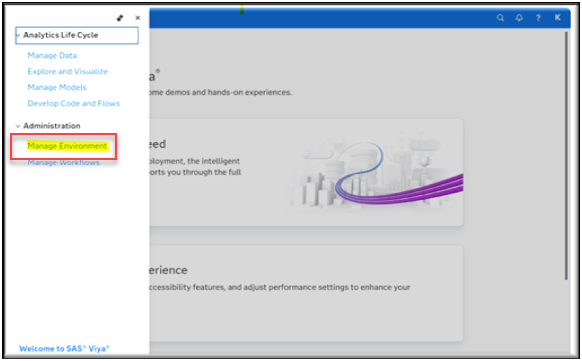
Navigate to Environment Manager by selecting the more menu from the Viya Welcome page.
Then select Manage Environment
This is the Administrator’s view of Viya Environment Manager.
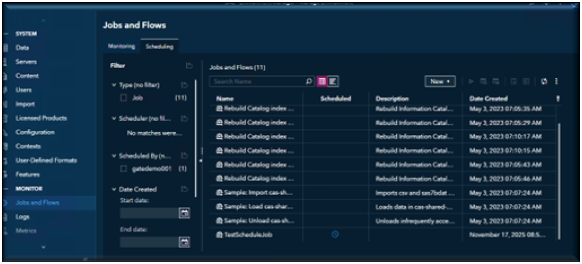
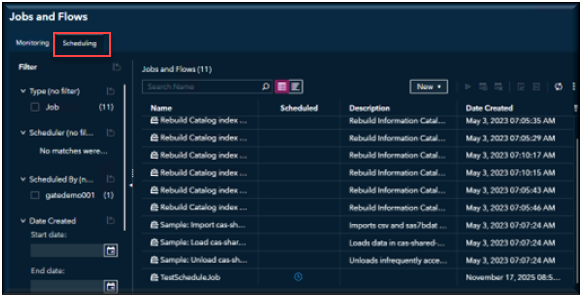
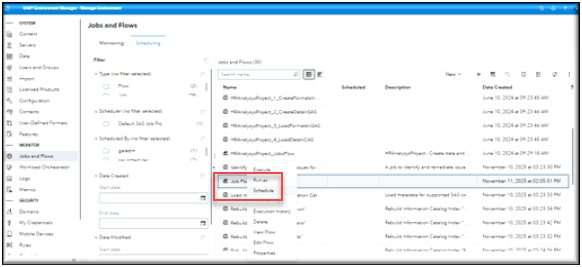
Navigate to the Jobs and Flows page. By default, the page will open in the Monitoring view. You will want to select the Scheduling View.
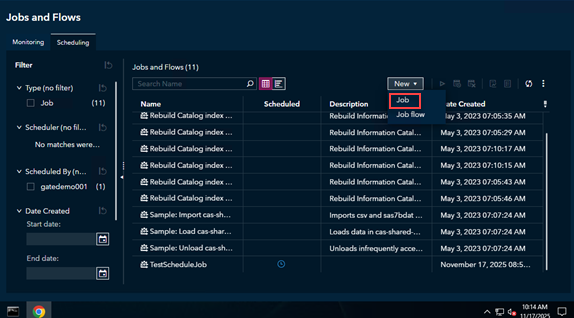
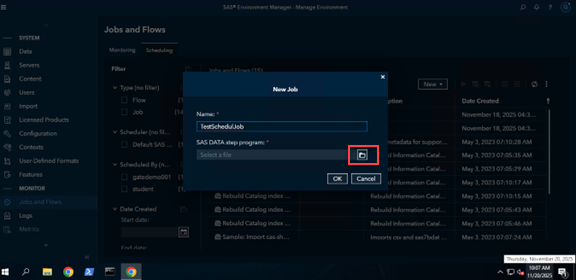
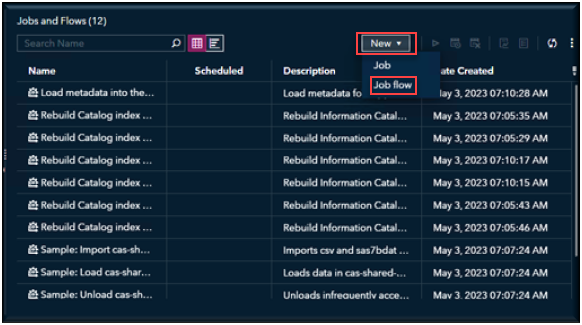
Select New -> Job from the pulldown menu.
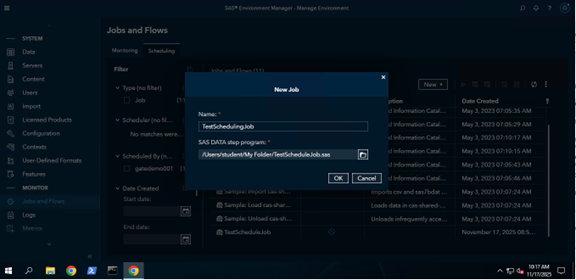
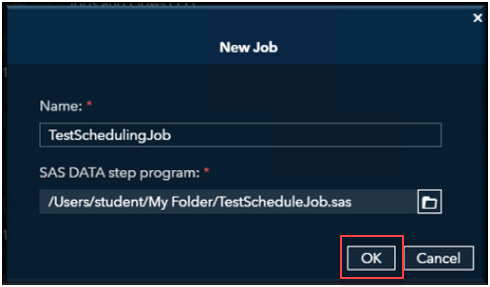
The New Job window will pop up. Fill in a Name you want give your Job.
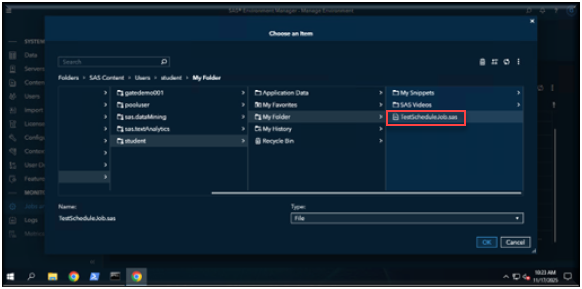
Select the location of the program you want to create a job for.
Navigate the folder of the Program you want to schedule.
Select OK.
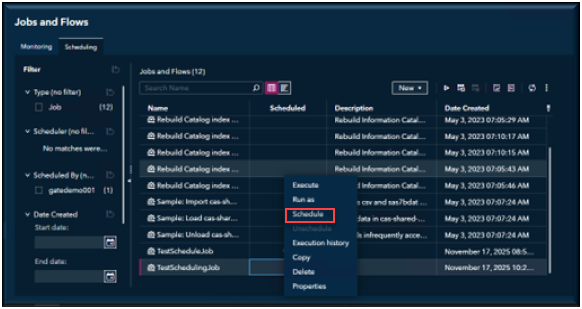
Now that you have completed the job creation steps, you will want to schedule the job.
How to Schedule a Job in SAS Viya
Here is how it works in a nutshell:
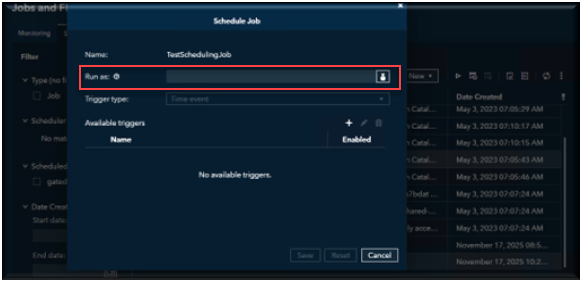
Open SAS Environment Manager and go to the Jobs and Flows page. Select the Schedule View, Select the job you want to automate, right Click on the Job and Select Schedule.
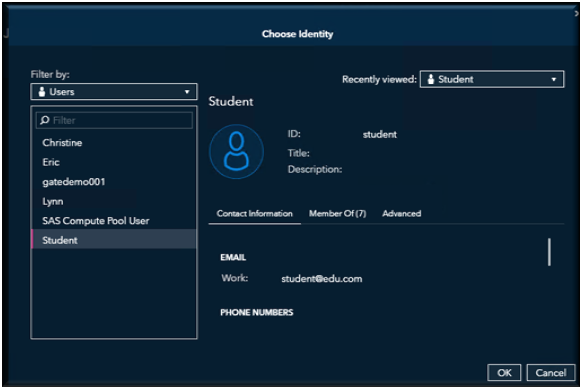
If you have Admin credentials and you want to run this scheduled job as another user, then select the icon on the “Run As” this will bring you to the list of available users.
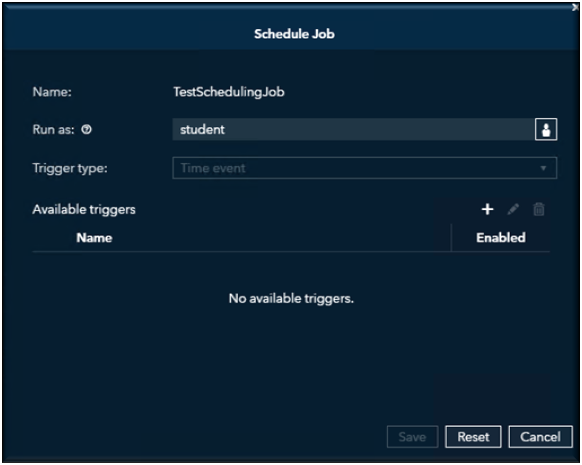
Select the user’s name you want to schedule and run this job for. This will only work if you have admin credentials. Once you have selected the id then select OK.
Now you can pick a time to schedule your job for, select the + (plus sign).
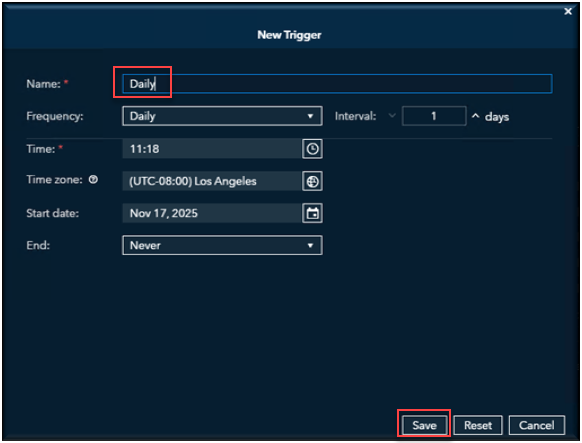
- Name: Daily News Digest Trigger
- (A descriptive name for the time-based trigger to easily identify it in the scheduler.)
- Frequency: Daily
- (The job will run daily.)
- Interval: 1 Day
- (It occurs every 1 day, meaning once per day.)
- Run Time: 08:00 AM
- (The job starts at 8:00 AM local time for morning execution.)
- Time Zone: America/New York (Eastern Standard Time)
- (Suitable for US East Coast operations; adjust if targeting a different region.)
- Start Date:
- End Date: you can select an exact date or never end the scheduled job.
(Runs through the end date period; set to a far-future date like "Never" if indefinite.)
This setup would trigger the job every day at the time you selected as well as the time zone AM EST, starting tomorrow and will run every week until you cancel the job. When complete, select save.
To verify your job has been scheduled, locate your job in the list of Jobs and Flows and verify that there is a blue clock icon next to the job under the Scheduled column.
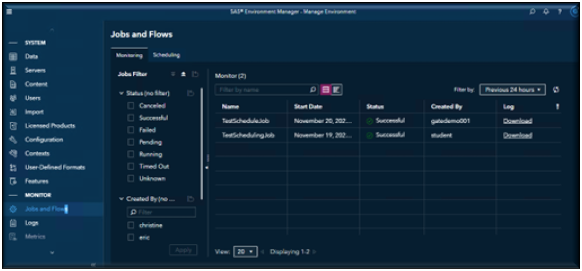
Monitoring Your Jobs
Once your jobs are scheduled, you can track their progress right in the interface. View (visualize when jobs ran and whether they succeeded or failed). You can zoom in by time and even filter by job name or date range.
Going Beyond Jobs: What Are Flows?
Sometimes when scheduling a job, a date and time trigger just is not enough. That is where job flows come in. A flow lets you connect multiple jobs together with conditions, so they run in sequence. For example, Job A loads data and Job B run analytics. Job B will only run after Job A finishes successfully. You can even build logic into your flows using AND /OR gates — it is like chaining tasks together into a smart, automated process.
Job flows are essential for enterprise-level scheduling, enabling reliable, repeatable automation of data processing pipelines, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) operations, reporting, and more. They go beyond single job scheduling by handling interdependencies and error handling.
Components of Job Flow
A flow can include:
- Jobs (SAS programs, data plans, imports)
- Job Flows Dependencies and connections (nested flows)
- Logic Gates (AND, OR conditions)
- Time Events (scheduled triggers)
- Command Line Actions (bash scripts or external commands)
Below is an example of a job flow created in the Jobs and Flows page of a Viya Environment Manager. This flow includes five jobs — a mix of SAS code, Data Explorer import tasks, and a Data Plan project — connected by two logic gates (one AND and one OR) and multiple connectors. The connectors (arrows) define job dependencies and determine the execution order. In this example, Jobs A, B, and C run at the same time when the flow starts. Job D runs only after Job C completes successfully, and Job E runs when Job D succeeds and either Job A or Job B finishes successfully.
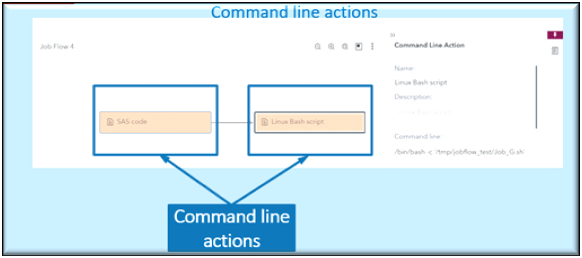
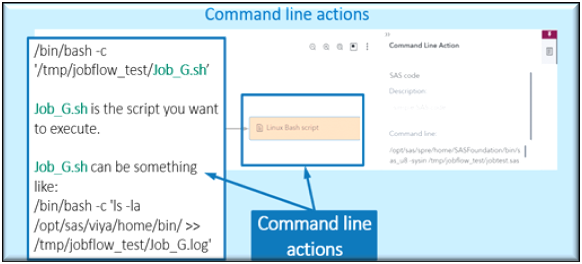
You can also include command-line action as part of a job flow. For example, this allows you to launch a SAS program in batch mode or run a Bash script directly from within the flow. Command-line actions can be saved to the Saved Actions area for reuse in other flows, making it easy to build on previous work. However, saved actions are user-specific and cannot be shared between different users.
This is an example of using the SAS Viya Command line as an Action in a Job Flow.
This is an example of using the SAS Viya Command line as an Action in a Job Flow.
This is an example of using A Lunix Bash command line as an Action in a Job Flow.
Creating a Job Flow
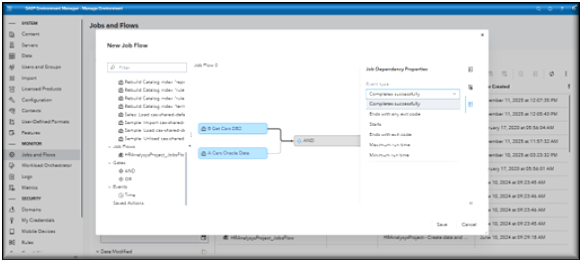
In Environment Manager navigate to the Jobs and Flow page, you will want to be in the Scheduling View. Just like when we create a new Job, we want to select New and from the list select Job Flow.
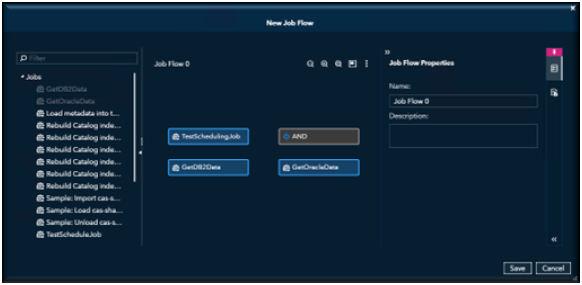
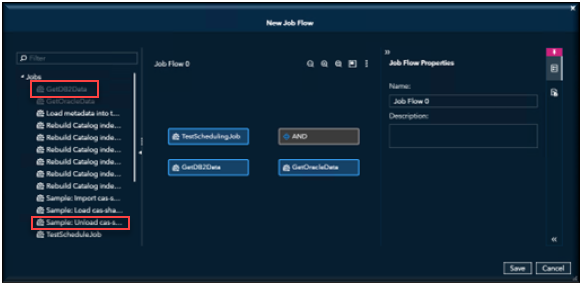
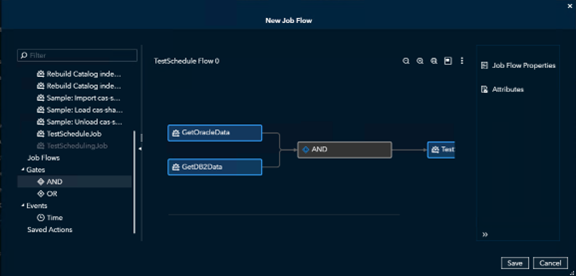
In the New Job Flow window, select objects that you want to add to the flow in the tree view and drag them to the flow editor.
In the New Job Flow window, select objects that you want to add to the flow in the tree view and drag them to the flow editor.
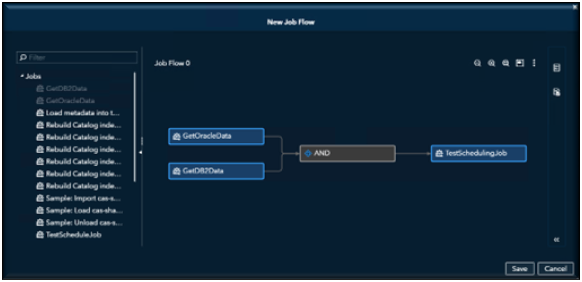
As you add objects to the flow, make connections between the objects to specify the sequence of the flow.
Click on the right side of the first object in the order and drag a line to the right side of the next object in the order.
Each object (other than gates) can have only one input connection and one output connection.
Objects change positions in the window automatically as you make connections.
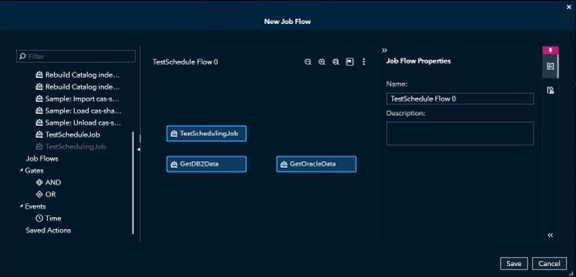
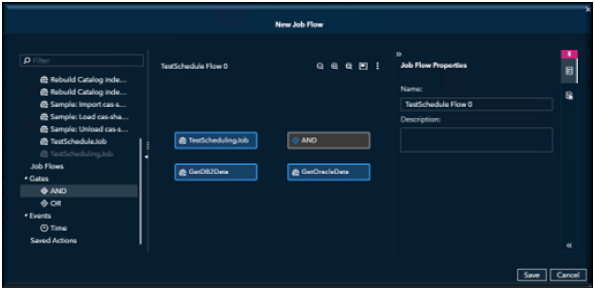
Adding an And Gate.
Connect them in the order you want each job to run.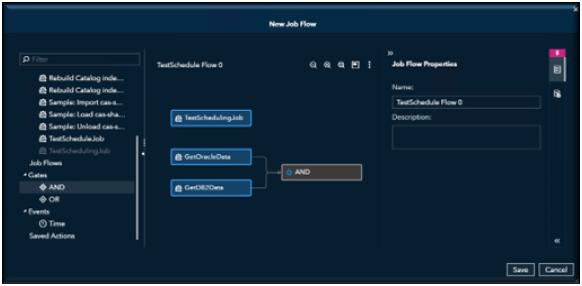
In this example, this is the order the jobs need to run; the first two jobs will be executed first and if they both run successfully then the last job will run.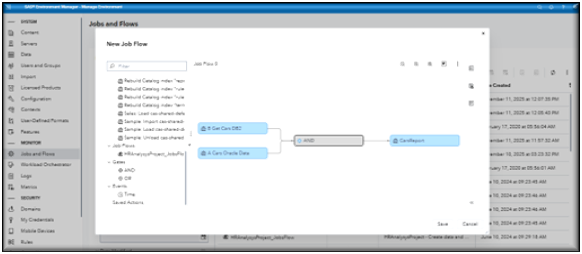
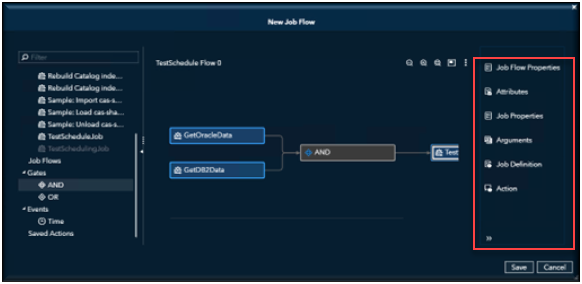
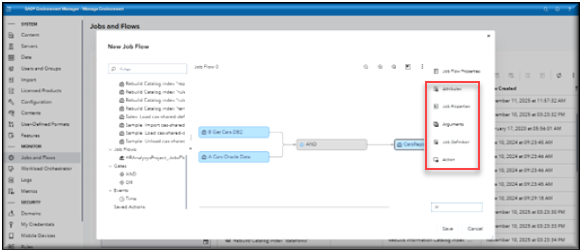
In this example, you can see additional options available in the right-hand menu. The options displayed depend on the section of the flow that you select, allowing you to customize and control various aspects of the flow’s functionality.
You can see additional options available on the right-hand menu. Once you have made all your selections you can save your flow.
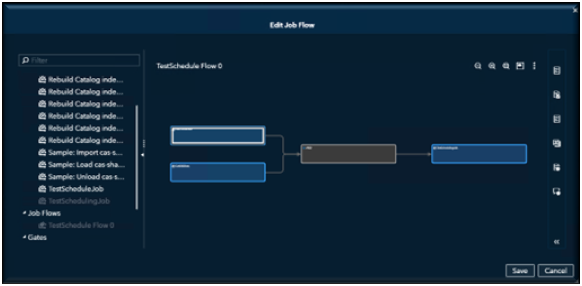
Once Saved, you can now schedule your flow jut like you scheduled your job.
For more information on Scheduling in Viya please visit this link SAS Help Center: SAS Viya Platform: Jobs and Flows.
Command Line Scheduling (For Power Users)
Prefer the command line? SAS Viya lets you run and schedule jobs using the CLI (Command Line Interface). You can create the same time-based triggers — down to minutes, hours, days, weeks, or months — right from your terminal. This is great for admins who like automation scripts or want to integrate Viya jobs into broader IT workflows.
For more information on scheduling Viya jobs using the command line click here SAS Help Center: Jobs and Flows: How To (CLI).