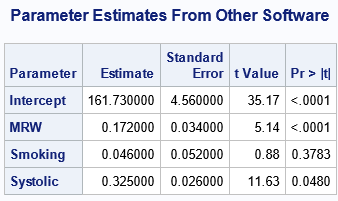
A previous article discusses standardized coefficients in linear regression models and shows how to compute standardized regression coefficients in SAS by using the STB option on the MODEL statement in PROC REG. It also discusses how to interpret a standardized regression coefficient. Recently, a SAS user wanted to know how