While the global pharmaceutical industry has been changing profoundly in the last 15 years, it has also been facing some huge challenges. Growing demand, increased competitiveness, reduced time to market, quality adherence and the spiralling cost of developing new drugs have increased pressure on pharma companies to deliver on tighter and tighter margins. But perhaps the most fundamental of these is addressing existing operational challenges across the end-to-end pharma value chain – i.e., R&D, manufacturing and distribution through technology-led continuous improvement and innovation.
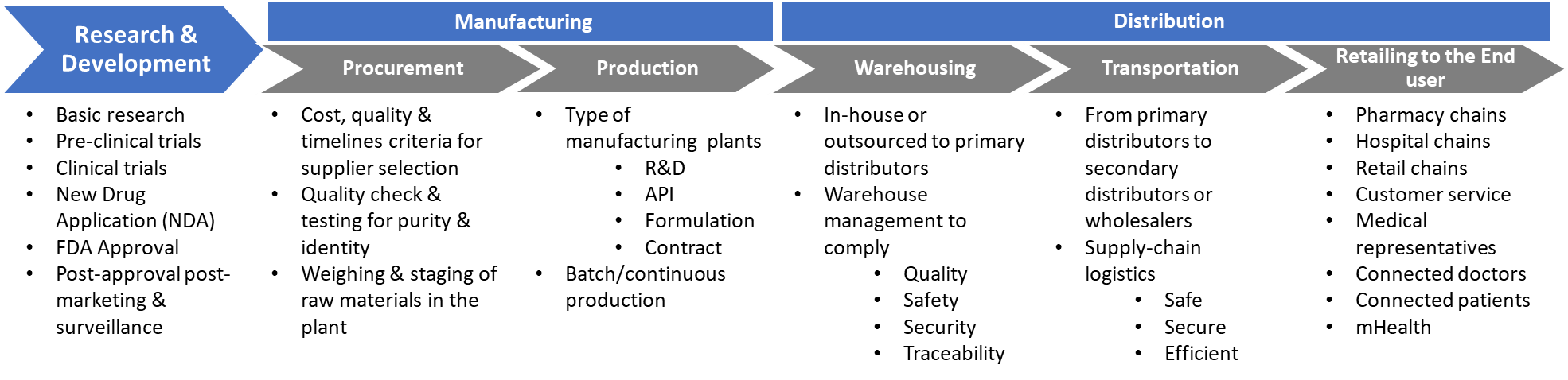
IoT technology coupled with the use of advanced analytics is revolutionising how pharma companies function. Across the globe, pharmaceutical developers and manufacturers are seeing the benefits of the technology in improved efficiency, fewer errors, faster time to market and less wastage. IoT analytics has the potential to change the whole operating model for pharma from research and development through manufacturing to distribution.

R&D
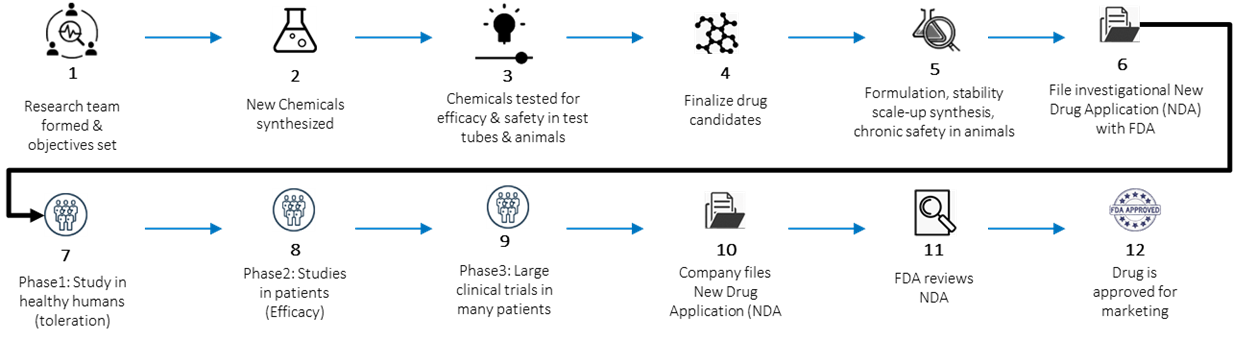
In R&D, IoT analytics is being used to reduce human error, increase efficiency and reduce waste. By improving real-time visibility while finalising drug candidates, increasing the availability of data during toleration and efficacy study, clinical trial spans are shortening and making it easier and quicker to get market authorisation for new drugs.
Fig: R&D indicative workflow.
R&D challenges
- Very people-intensive processes in R&D, which increase the potential for human error.
- Long development times for new drugs and getting existing drugs licensed for other uses.
R&D IoT analytics use cases
- Smart lab or connected lab for instrument utilisation and maintenance, process optimisation, anomaly detection and controlled output quality.
- Clinical trial optimisation using IoT devices (wearables) through real-time monitoring.
- Clinical trial success rate prediction and prescription.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, pharma companies are seeing the benefits of improving stock control, quality and processes by use of IoT technology. All three are helping to increase efficiency and, therefore, yield. As in any other manufacturing sector, IoT technology also supports better use of assets. In particular, identifying machines that need maintenance ahead of breakdowns means that stoppages are avoided, and maintenance can be scheduled for quieter times.
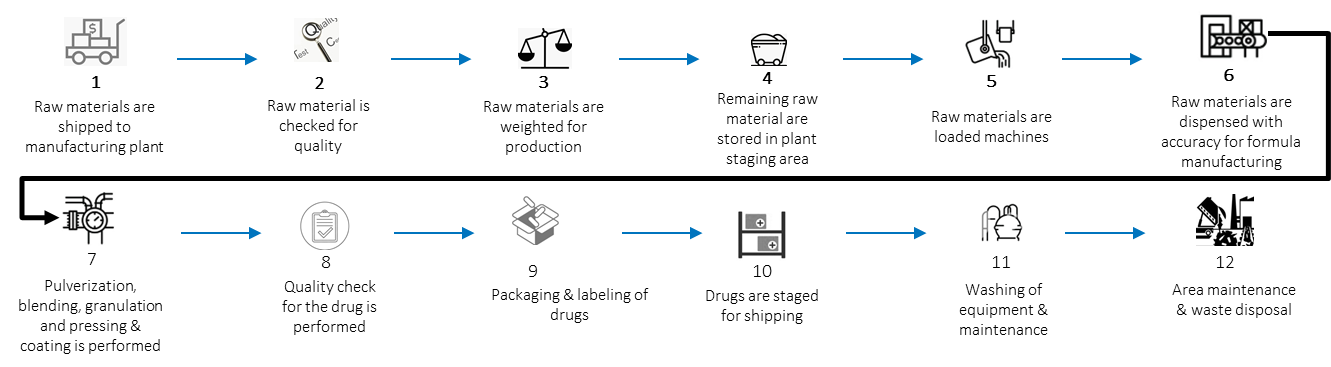
Manufacturing challenges
- Variable quality of raw materials, partly because of sourcing, and partly because of potential contamination.
- Theft or damage of raw materials in transit or during storage, which in turn will affect the quality of the finished product.
- Poor consistency of product quality because of uncertainties about raw material quality and changes in manufacturing processes.
- Unplanned manufacturing downtime because of machine breakdowns.
Manufacturing IoT analytics use cases
- Demand forecasting of raw material based on inventory quantity and quality.
- Raw material optimisation by real-time monitoring to reduce damage, wastage and pilferage.
- Digital twin of manufacturing equipment monitoring.
- Preventive and predictive maintenance of plant equipment.
- Real-time centralised monitoring for batch processing and continuous manufacturing.
- Monitoring and controlling drug manufacturing environmental ambient conditions.
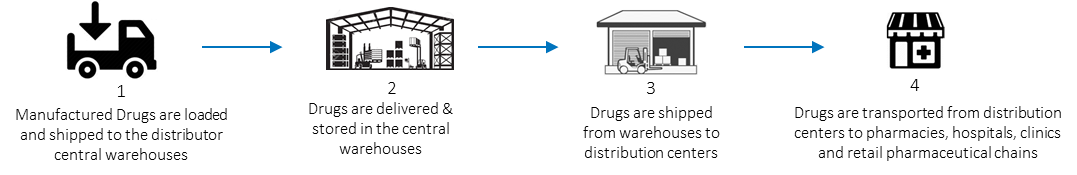
Distribution
In distribution, better stock management is leading to less wastage and lower inventory. In turn, this means better use of space in warehouses – and potentially lower storage costs. More importantly, however, IoT technology is improving supply chain and transit visibility. The most obvious benefit is that this makes it easier to get drugs to patients. However, it also helps to improve security, making it harder to counterfeit drugs, and protecting pharma companies’ investment in R&D for longer.
Distribution challenges
- High levels of inventory in warehouses and stores, tying up funds and leading to waste.
- Damage and/or theft of drugs in storage or transit.
- Limited visibility of drugs across the supply chain, making them hard to trace.
- High levels of counterfeit drugs, reducing profitability.
- Unavailability of prescribed medicines in hospitals or pharmacies.
Distribution IoT analytics use cases
- Smart warehouse management systems.
- Locating inventory in real time.
- Improving utilisation of warehouse assets such as forklifts, stackers, etc.).
- Monitoring and controlling ambient and drug-specific conditions (temperature, humidity, etc.).
- Predictive modelling to optimise order fulfilment.
- Smart warehousing and routing using automated guided vehicles and automatic mobile robots (AMRs).
- Smart supply chain.
- Real-time tracking of logistics and transportation.
- Remote shipment environment monitoring (cold chain, etc.).
- Smart serialisation through AIDC (automatic identification and data capturing).
- Reverse supply chain traceability for hazardous waste.
- Smart vending machines, enabling accurate demand forecasting.
Convergence of life sciences and health care
Addressing the above operational challenges using IoT and advanced analytics is just the beginning of a pharmaceutical digital revolution. The future lies in achieving closer integration between what we might call "life sciences" – pharmaceuticals, medical devices and biotechnology – and more traditional health care delivery.
Future lies in achieving closer integration between what we might call ‘life sciences’—pharmaceuticals, #medical devices and #biotechnology—and more traditional healthcare delivery Share on X
New technology products are changing how we view medicine and health care by crossing the boundaries between the two. These include ingestible pills with microcameras, implants connected to IoT devices, more conventional wearables, smart medical equipment, and apps that connect patients and doctors in real time, to name a few. The explosion of data from all these sources means that the distinction between the two is becoming increasingly academic.
The combination of a growing market and recognition of the importance of innovation and efficiency means that investment in technology is also increasing. There is growing recognition that moving down this route is the way to the future. Companies that have started down this path are seeing wins already.
Discover more insights on connected manufacturing and AIoT on our IIoT Information Hub.