SAS allows for three different cube storage mechanisms:
1. MOLAP
The traditional SAS OLAP Cube will all aggregations / nway stored on a physical file structure accessible by the SAS OLAP Cube Server.
2. ROLAP
A relational OLAP cube - where no aggregations are stored and SAS points to the RDBMS table structures.
3. HOLAP
A hybrid OLAP approach that offers a bit of both worlds.
As a team of SAS and Teradata knowledge leaders write in the 2009 User Group Paper "
Using SAS OLAP Server for a ROLAP Scenario", the advantanges of going with ROLAP include immediate data update availability to OLAP users, using dramatically smaller storage space and reducing build times required for the OLAP Cube.
But how do you build one?
The steps are pretty straightforward and almost too easy.
- Utilize source tables from RDBMS System (SQL, Oracle, etc) that are defined in SAS Metadata
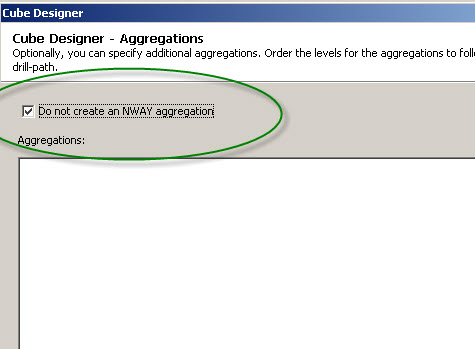
- Select ‘Do not create an NWAY aggregation’ checkbox on Aggregation Screen in OLAP Cube Editor


2 Comments
Pingback: To be or not to be, testing your cube’s existence - Real BI for Real Users
Pingback: OLAP users can fall into the abyss of detail data - Real BI for Real Users