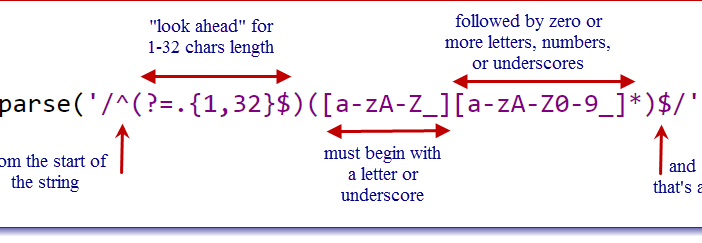
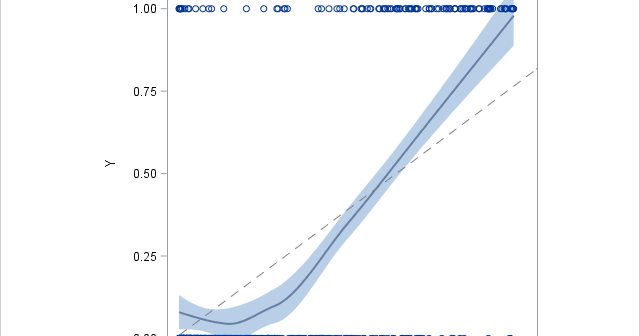
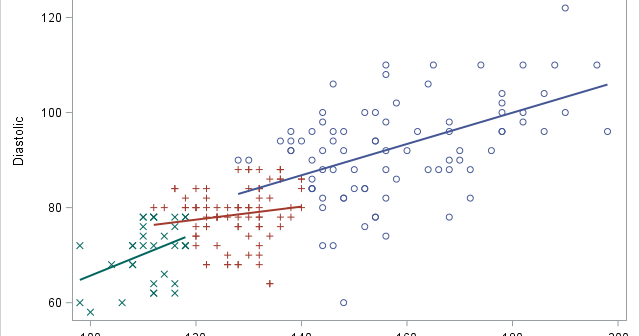
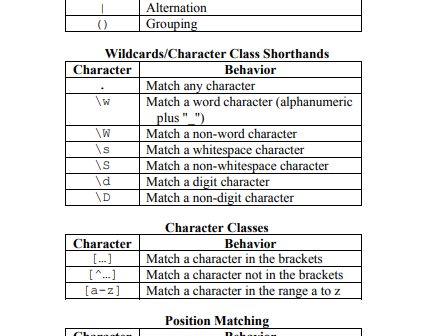
Every year at Halloween, I post an article that shows a SAS trick that is a real treat. This article shows how to use the INTNX function to find dates that are related to a specified date. The INTNX function is a sweet treat, indeed. I previously wrote an article