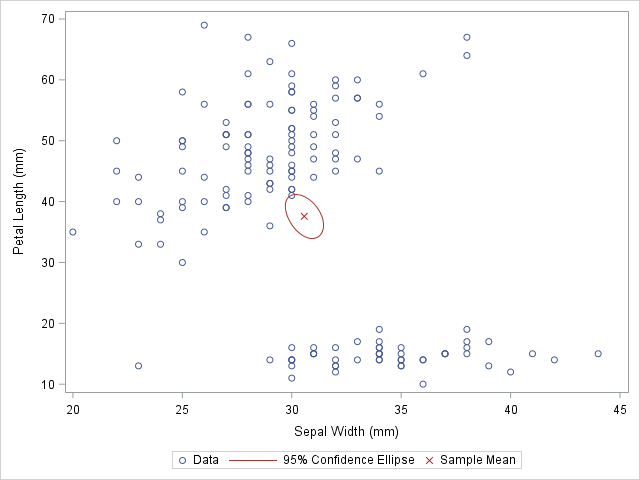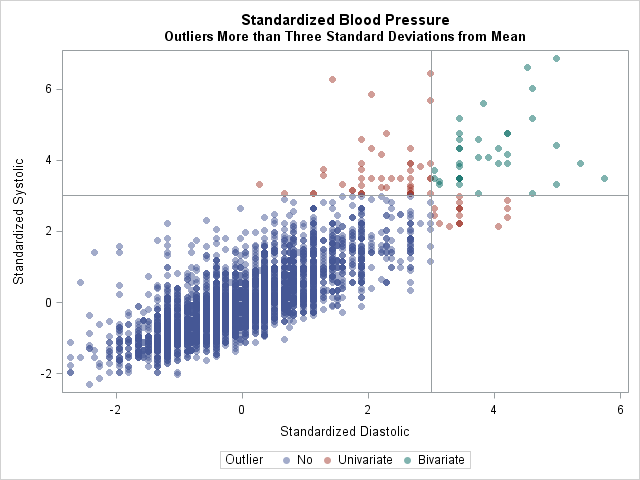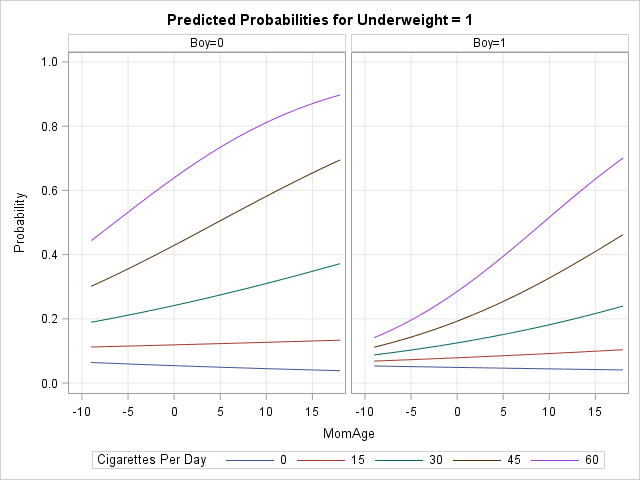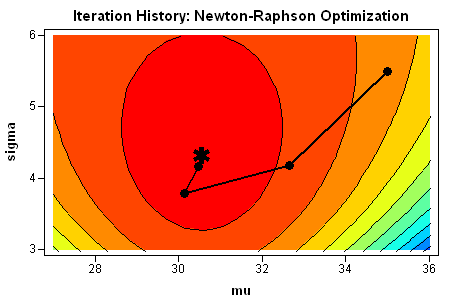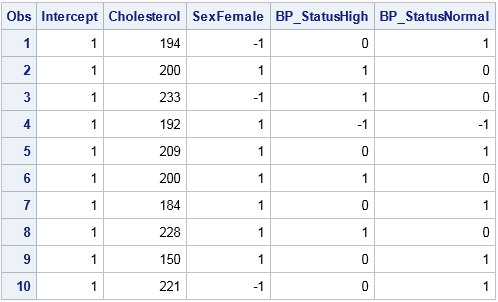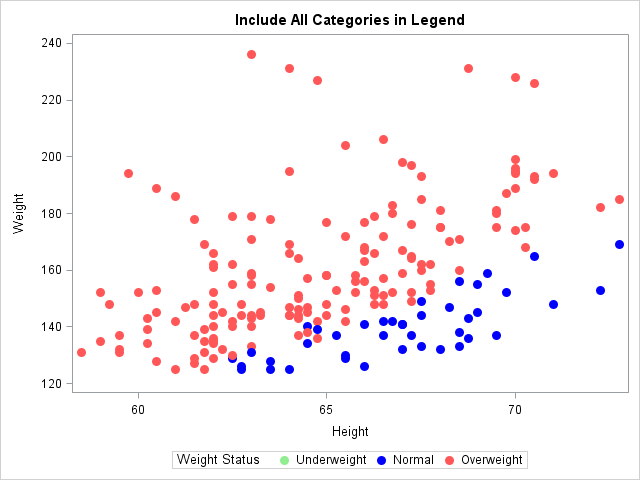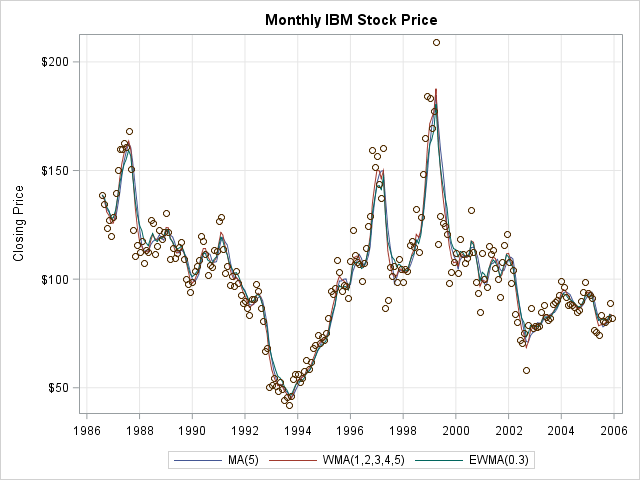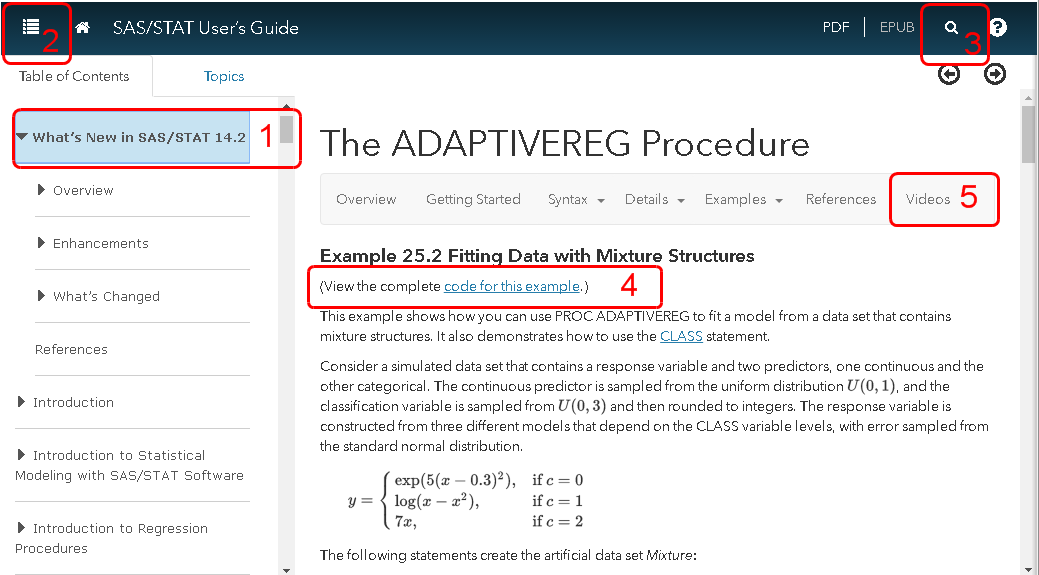
The SAS analytical documentation has a new look. Beginning with the 14.2 release of the SAS analytical products (which shipped with SAS 9.4m4 in November 2016), the HTML version of the online documentation has moved to a new framework called the Help Center. The URL for the online documentation is