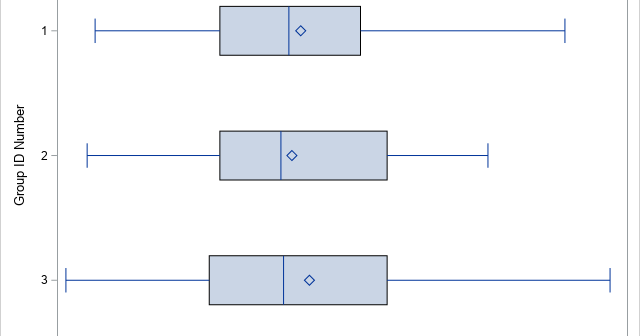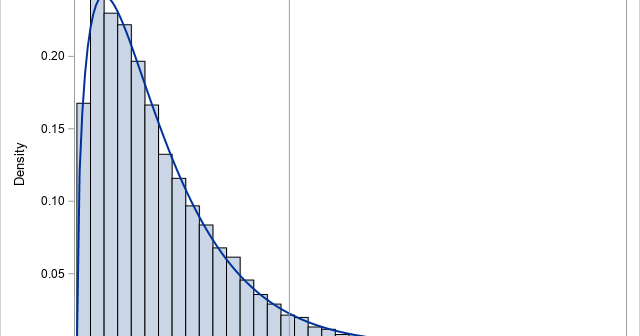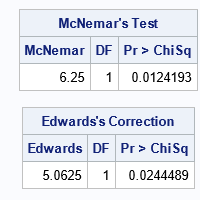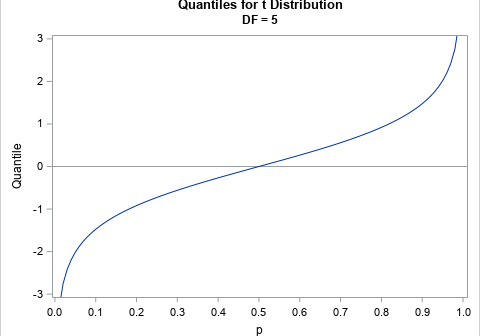
Recently, I needed to solve an optimization problem in which the objective function included a term that involved the quantile function (inverse CDF) of the t distribution, which is shown to the right for DF=5 degrees of freedom. I casually remarked to my colleague that the optimizer would have to