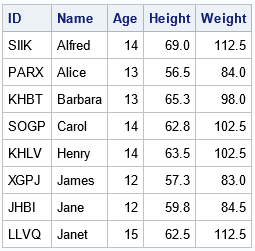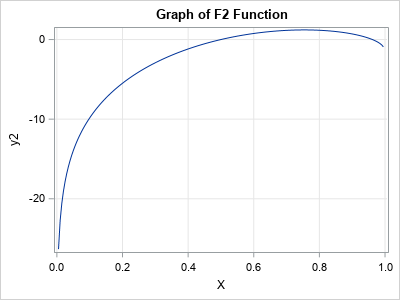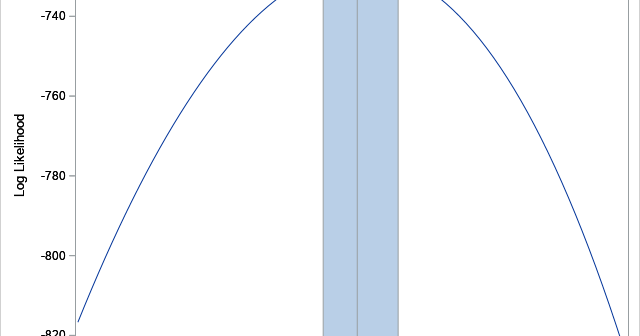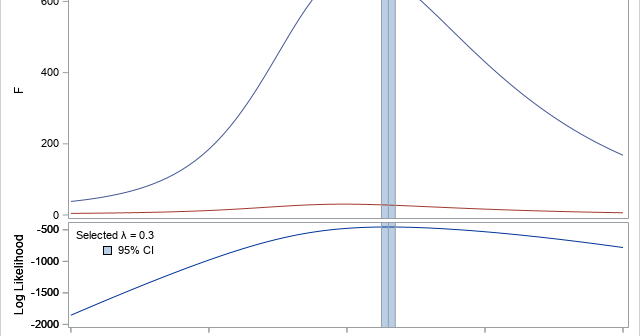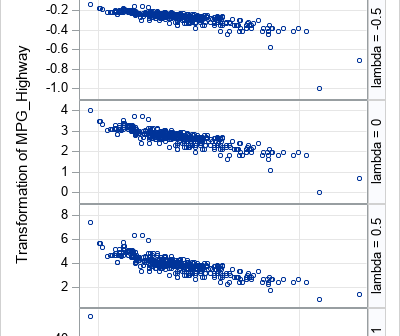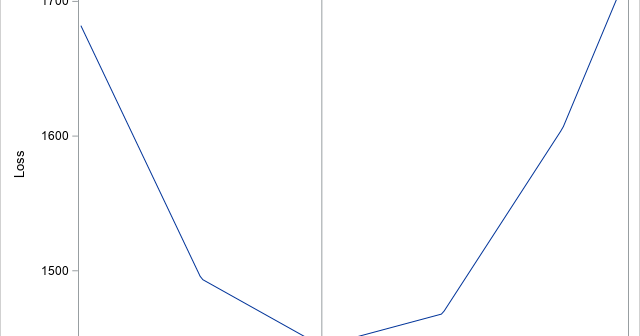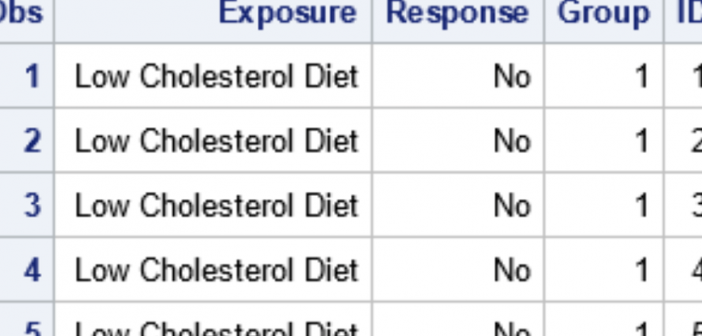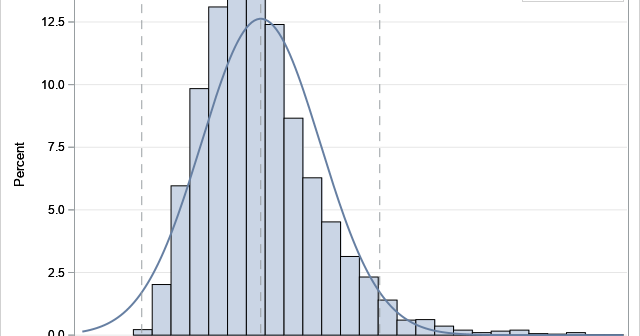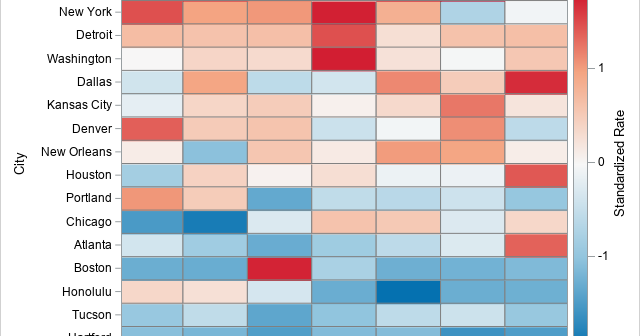
A profile plot is a compact way to visualize many variables for a set of subjects. It enables you to investigate which subjects are similar to or different from other subjects. Visually, a profile plot can take many forms. This article shows several profile plots: a line plot of the