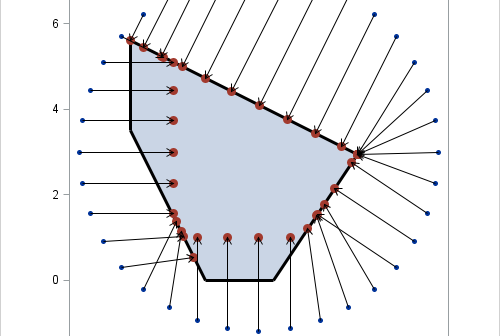
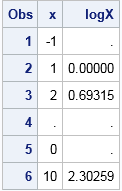
My presentation at SAS Global Forum 2017 was "More Than Matrices: SAS/IML Software Supports New Data Structures." The paper was published in the conference proceedings several months ago, but I recently recorded a short video that gives an overview of using the new data structures in SAS/IML 14.2: If your