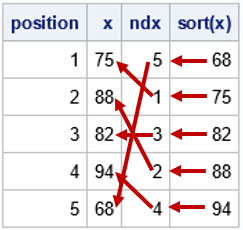
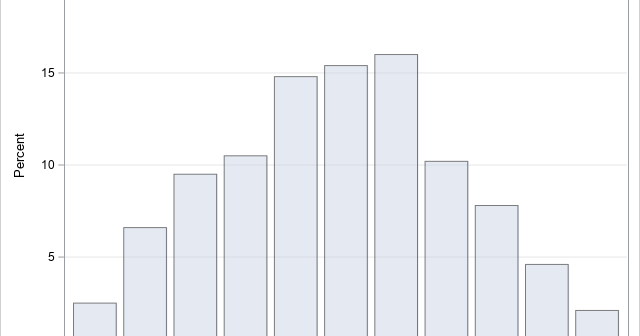
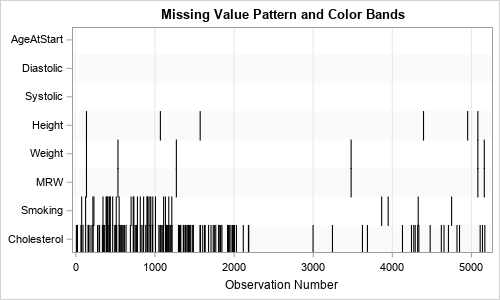
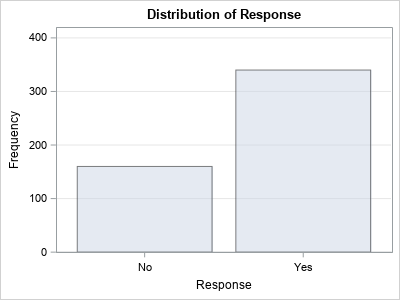
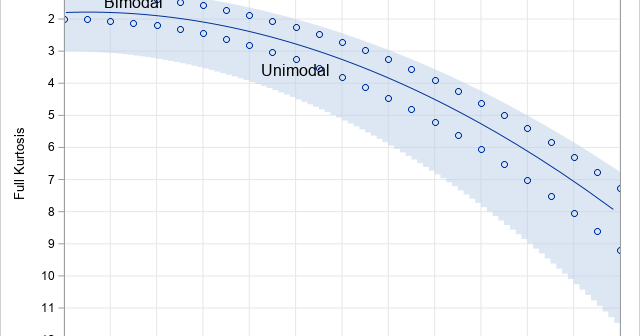
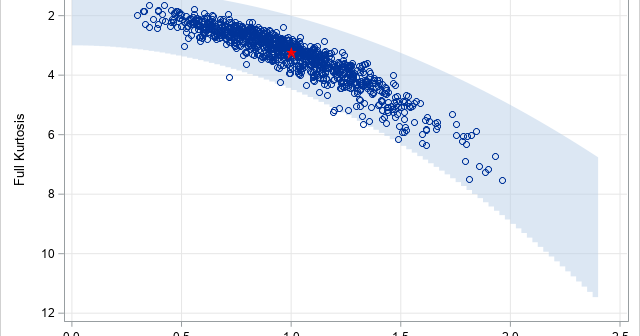
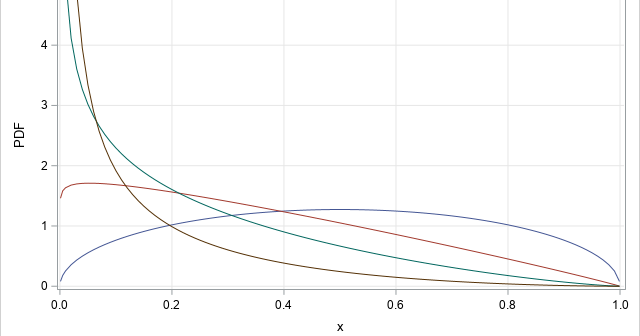
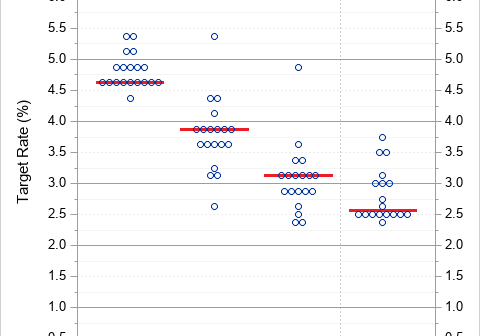
After writing a program that simulates data, it is important to check that the statistical properties of the simulated (synthetic) data match the properties of the model. As a first step, you can generate a large random sample from the model distribution and compare the sample statistics to the expected