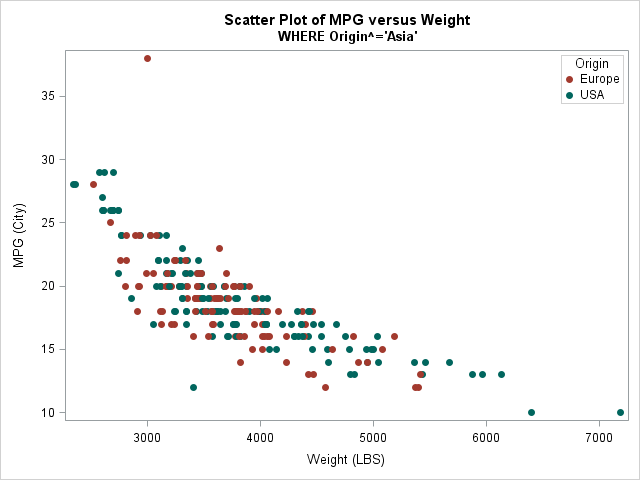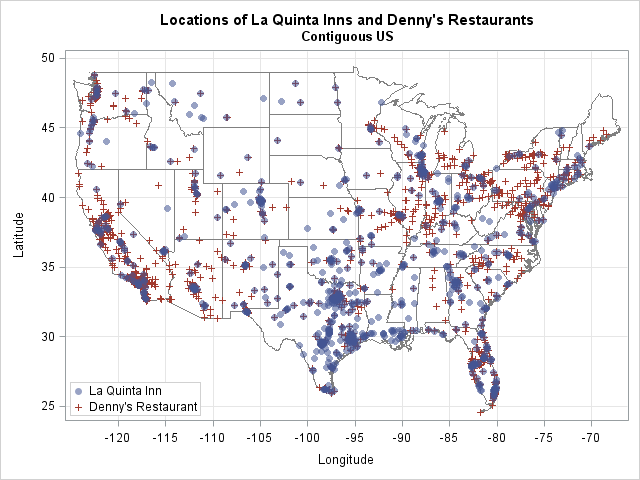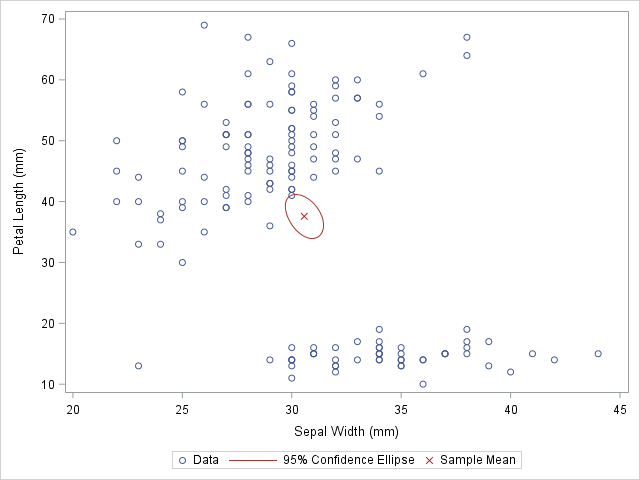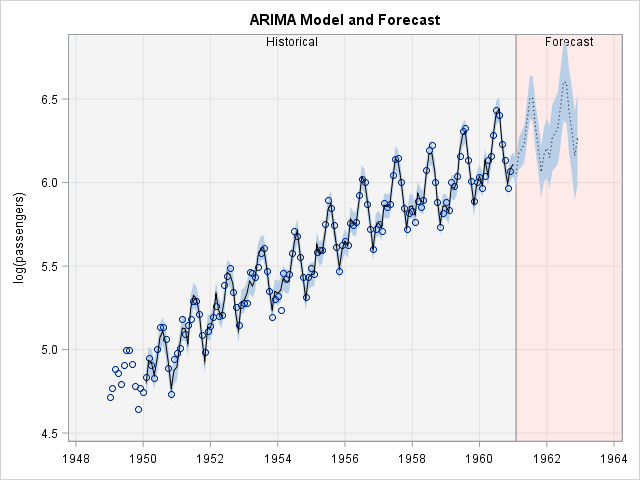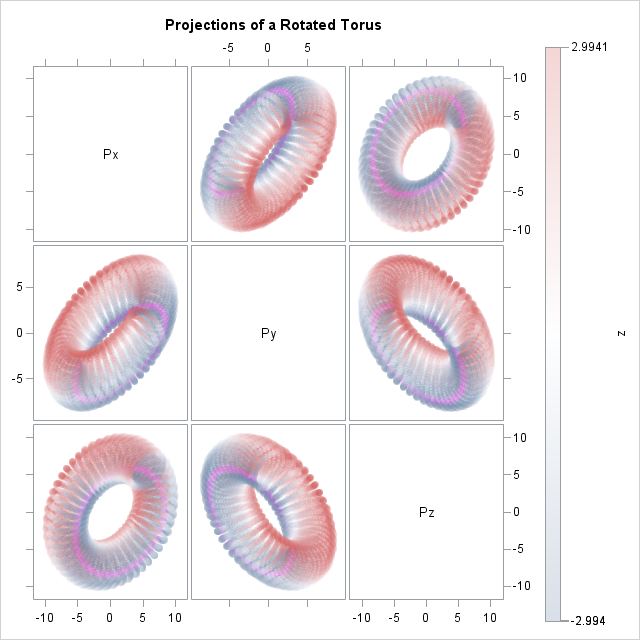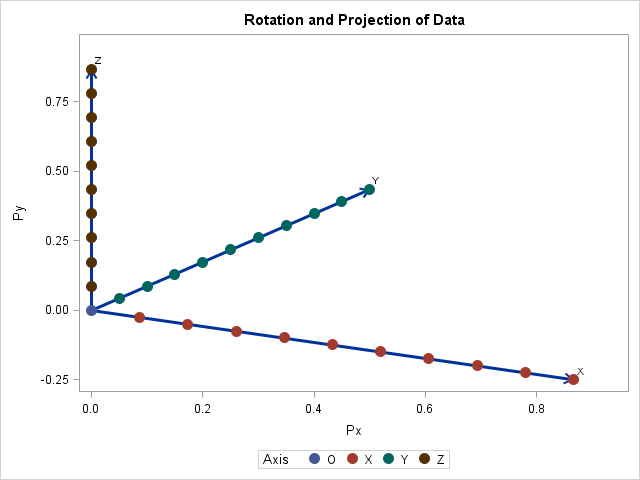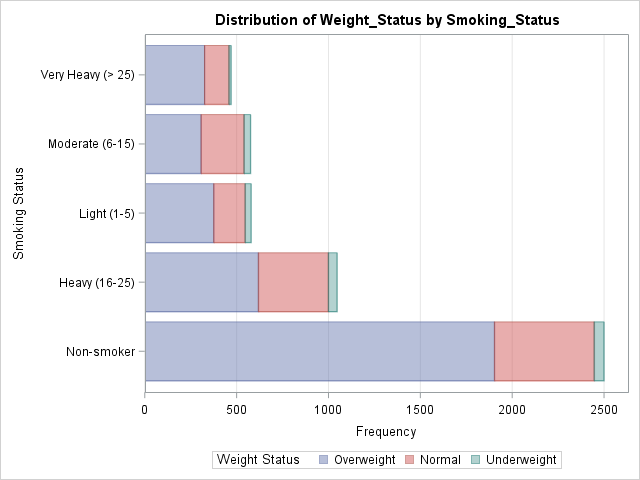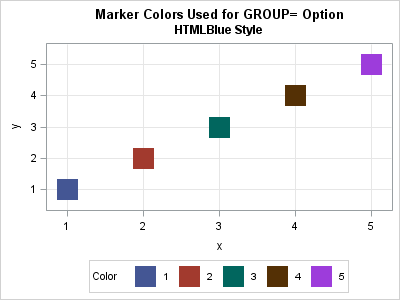
Suppose you create a scatter plot in SAS with PROC SGPLOT. What color does PROC SGPLOT use for the markers? If you specify the GROUP= option so that markers are colored by a grouping variable, what colors are used to represent the various groups? The following scatter plot shows the