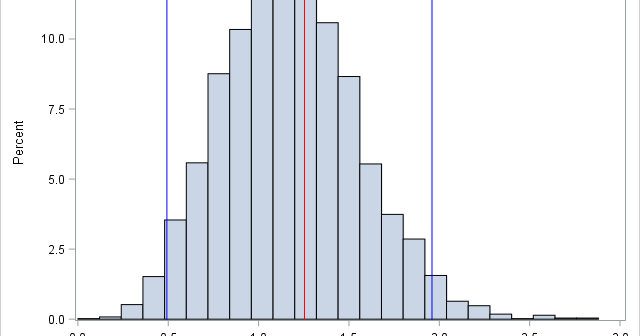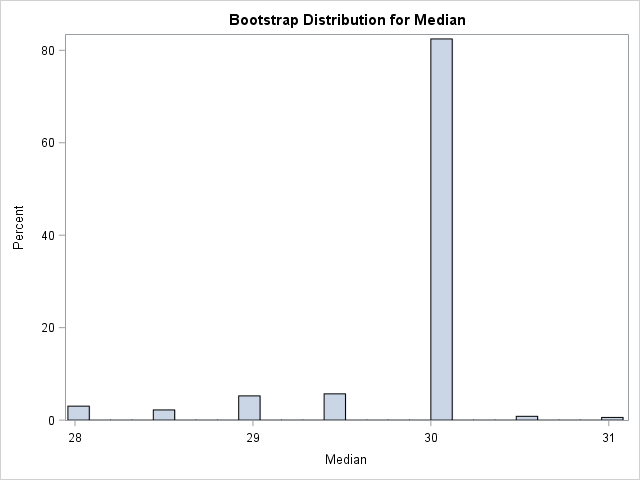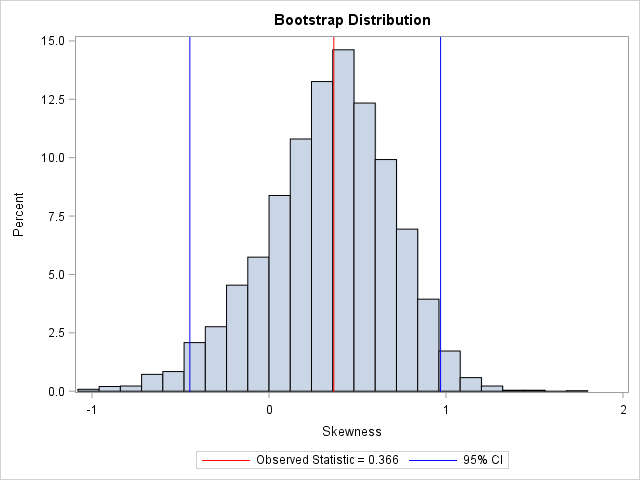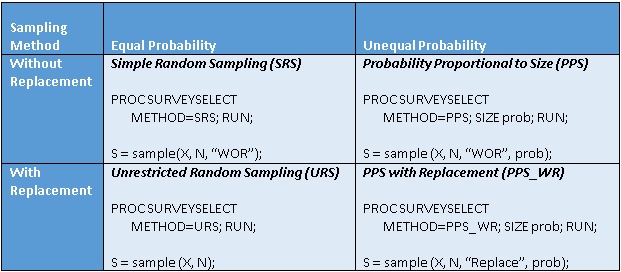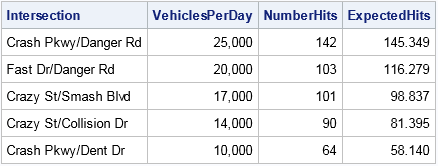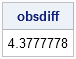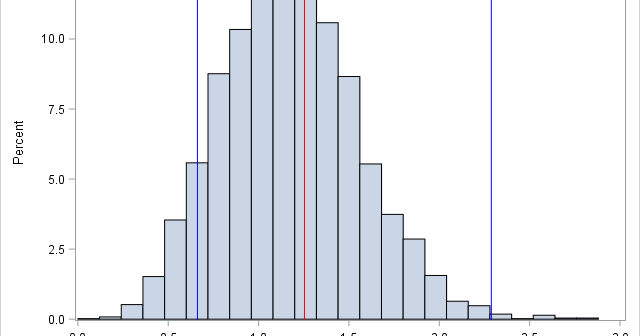
I recently showed how to compute a bootstrap percentile confidence interval in SAS. The percentile interval is a simple "first-order" interval that is formed from quantiles of the bootstrap distribution. However, it has two limitations. First, it does not use the estimate for the original data; it is based only