 If you'd like to extend your investment in the Hadoop infrastructure, SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop can help by enabling you to colocate SAS Grid jobs on your Hadoop data nodes. It works because SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop – which is Cloudera certified – is integrated with the native components of your Hadoop ecosystem, specifically YARN and Oozie.
If you'd like to extend your investment in the Hadoop infrastructure, SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop can help by enabling you to colocate SAS Grid jobs on your Hadoop data nodes. It works because SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop – which is Cloudera certified – is integrated with the native components of your Hadoop ecosystem, specifically YARN and Oozie.
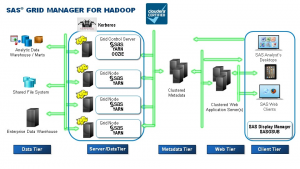
How does it work? The SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop conceptual architecture diagram shown below illustrates the various tiers in a complete SAS deployment. Note that the Cloudera Hadoop cluster and the SAS Grid components are colocated on the same hardware, making this both a data and a server tier. Kerberos is also a required component in this environment.
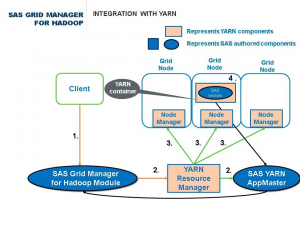
The next diagram outlines the steps that happen from Point A (a SAS client application makes a request to SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop to run a SAS Grid job) to Point B (YARN runs the SAS Grid job in a YARN container). In this diagram, the blue components are authored by SAS and the beige components are part of the YARN ecosystem. The SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop module and SAS YARN AppMaster are all part of the SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop product. Let's review the details of the integration between SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop and YARN.
The following steps correspond to the numbers on the diagram above:
- A SAS client submits a SAS job (SASGSUB, CONNECT, grid-launched workspace server) to the SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop module.
- The SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop module communicates with the YARN resource manager to invoke the SAS YARN application master.
- The SAS YARN application master requests a YARN container with the specified resources. The resources are specified in a grid policy file read by SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop. When the YARN Resource Manager determines which node has the resources, the application master requests a YARN container on the grid node that has the available resources.
- YARN runs the command it was given to invoke SAS under the control of the YARN container.
- Once the SAS Grid job has started, the remaining SAS Grid behavior is unchanged. YARN knows which resources are used by the SAS Grid job, allowing you to build a multitenant or shared Hadoop cluster.

The bottom line: SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop lets organizations manage diverse workloads on a shared Hadoop cluster. By using YARN, long processes can run with batch and ad hoc processes without contending for resources. But each workload has different service level agreements (SLAs). So, during the day, a nightly batch job run should not stop an important real-time analysis job from running and should not significantly hamper exploration jobs performed by R&D.
Watch for the next post in this series to hear from Farzana Kader about how Cloudera Manager and YARN can be used to manage these different workloads.

2 Comments
Are there any plans to integrate Grid Manager for Hadoop with the Hortonworks Data Platform in future releases?
Thanks for asking about this. Actually SAS Grid Manager for Hadoop already supports Hortonworks (and we are certified with them as well). The focus of this blog was on Cloudera because this was Part 1 in a 2 part blog series done in conjunction with Cloudera. However, you can find all the support details here: http://support.sas.com/rnd/scalability/grid/hadoop/index.html .