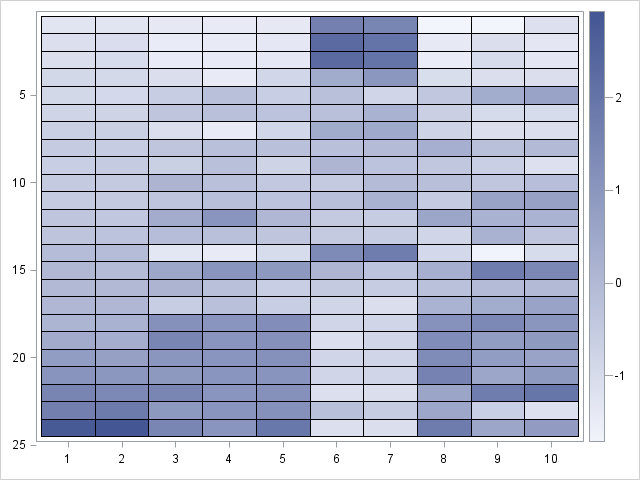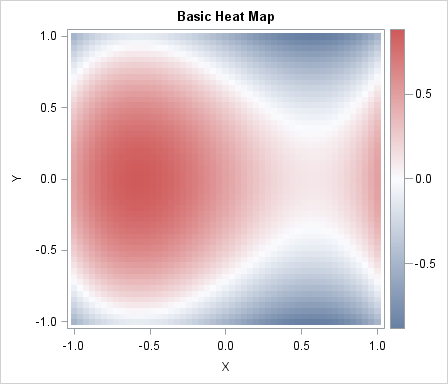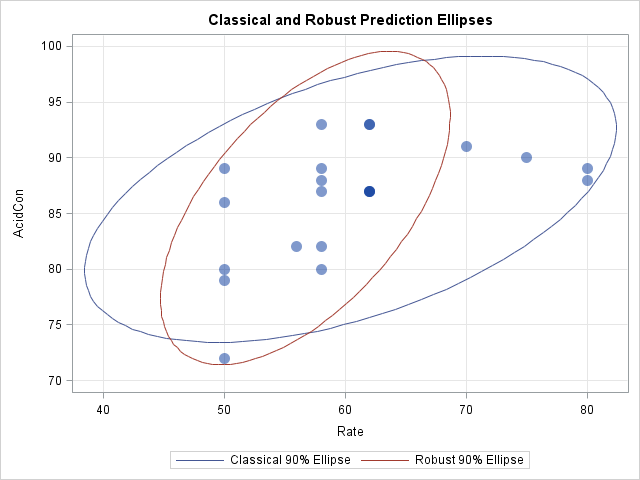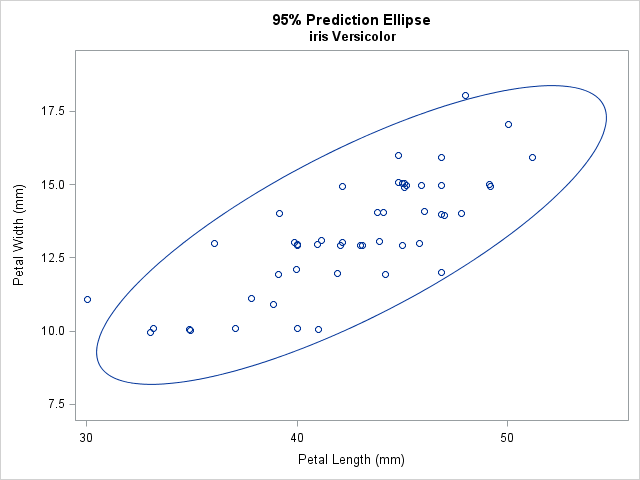
Have you ever looked as a statistical graph that uses bright garish colors and thought, "Why in the world did that guy choose those awful colors?" Don't be "that guy"! Your choice of colors for a graph can make a huge difference in how well your visualization is perceived by