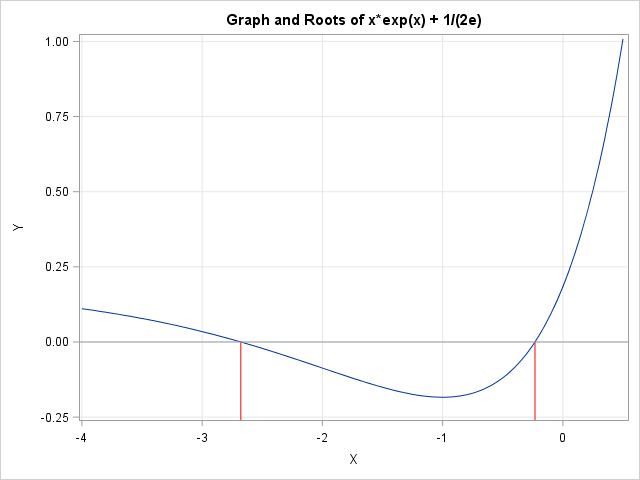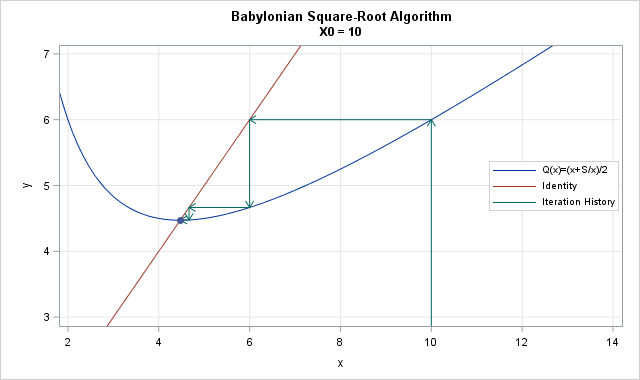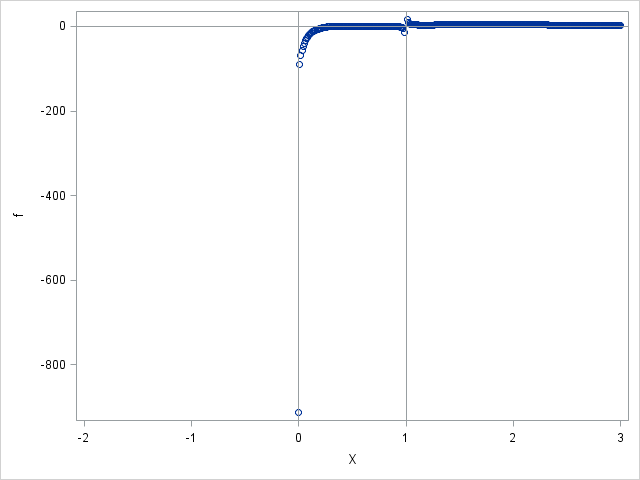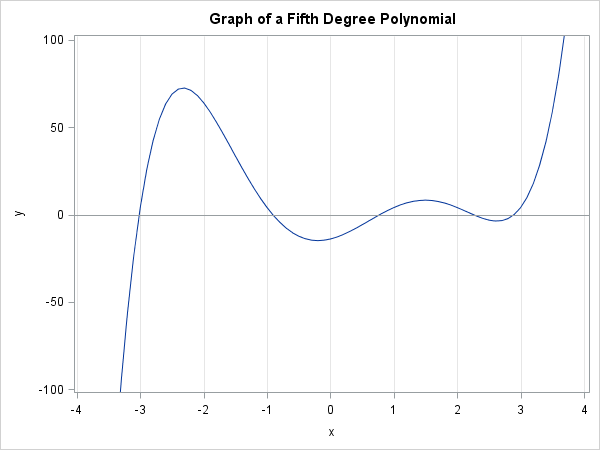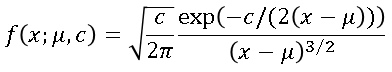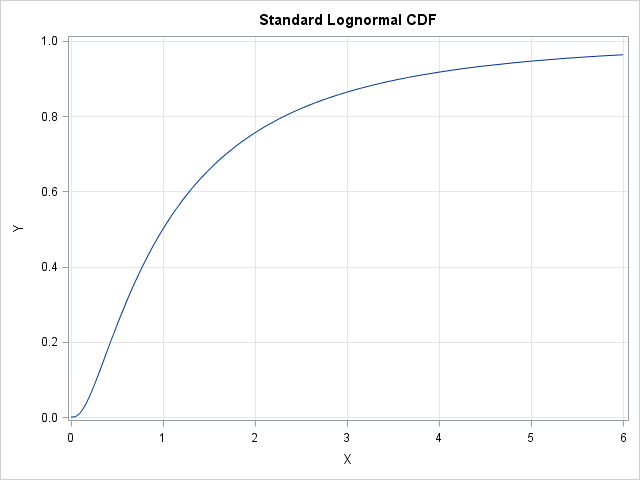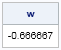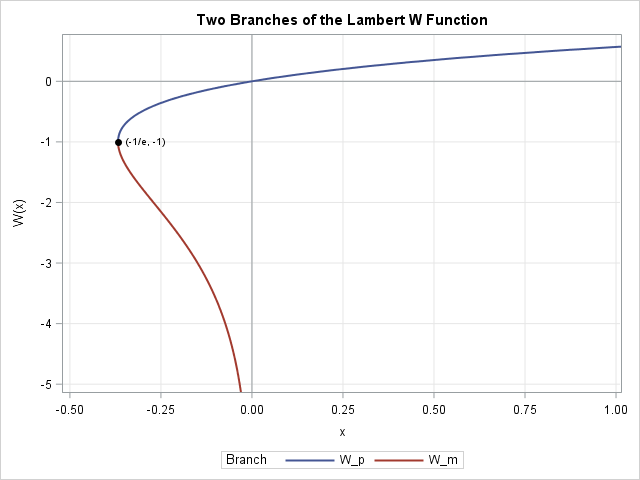
This article describes how you can evaluate the Lambert W function in SAS/IML software. The Lambert W function is defined implicitly: given a real value x, the function's value w = W(x) is the value of w that satisfies the equation w exp(w) = x. Thus, W is the inverse