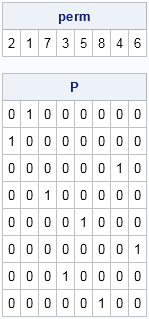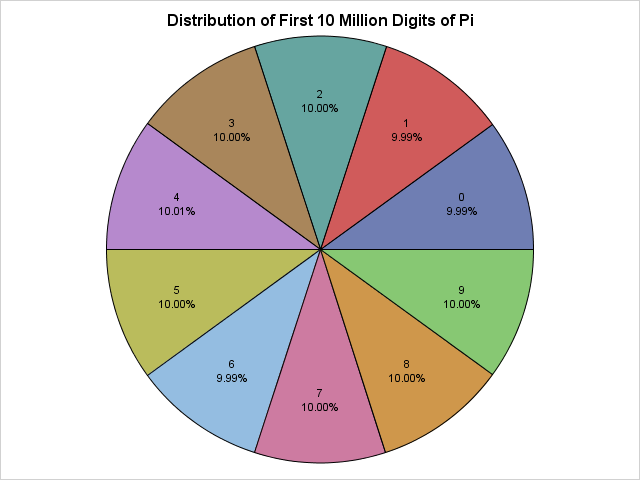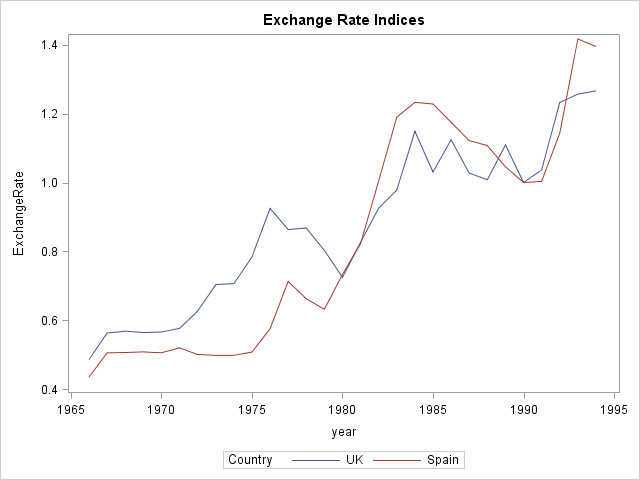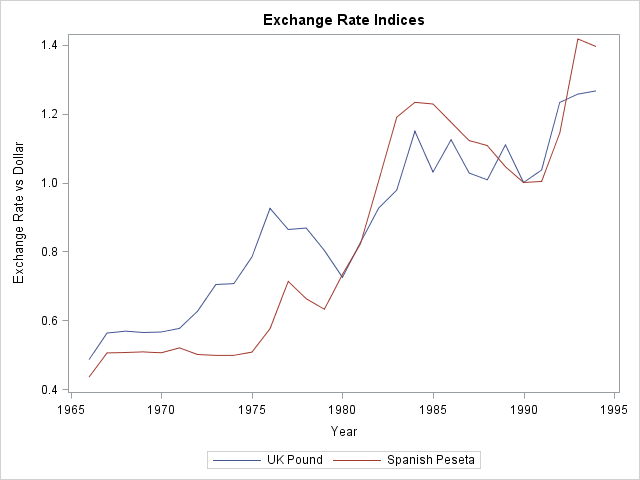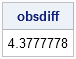
Perhaps you saw the headlines earlier this week about the fact that it has been nine years since the last major hurricane (category 3, 4, or 5) hit the US coast. According to a post on the GeoSpace blog, which is published by the American Geophysical Union (AGU), researchers ran