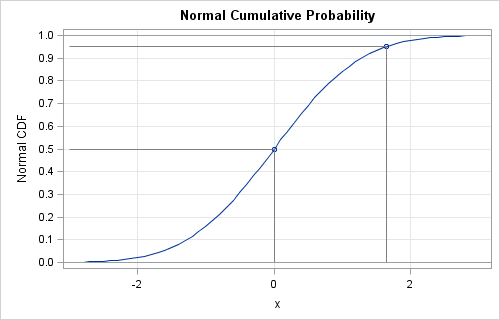
Howard Wainer, who used to write the "Visual Revelations" column in Chance magazine, often reminded his readers that "we are almost never interested in seeing Alabama first" (2005, Graphic Discovery, p. 72). His comment is a reminder that when we plot data for a large number of categories (states, countries,