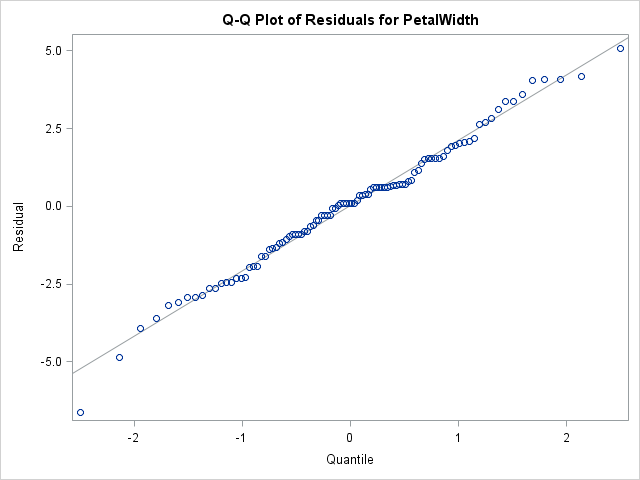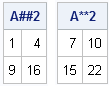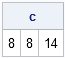
The SAS/IML language supports user-defined functions (also called modules). Many SAS/IML programmers know that you can use the RETURN function to return a value from a user-defined function. For example, the following function returns the sum of each column of matrix: proc iml; start ColSum(M); return( M[+, ] ); /*