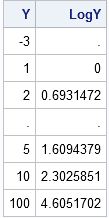
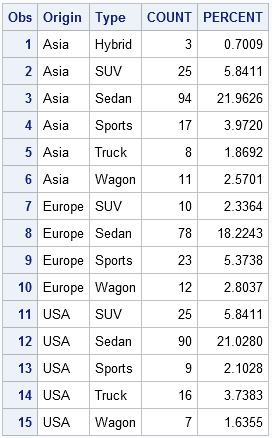
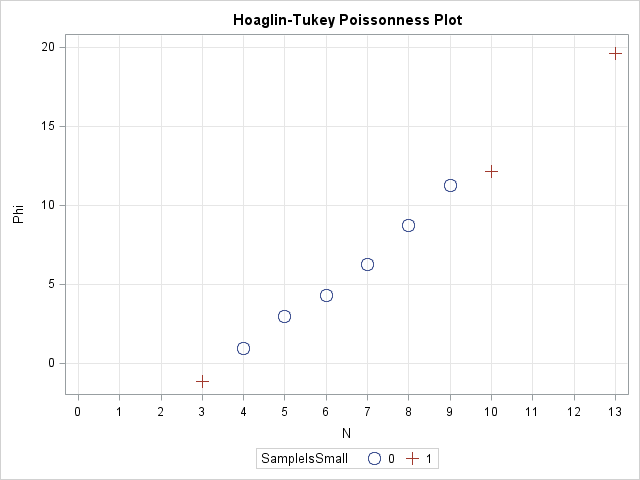
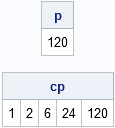
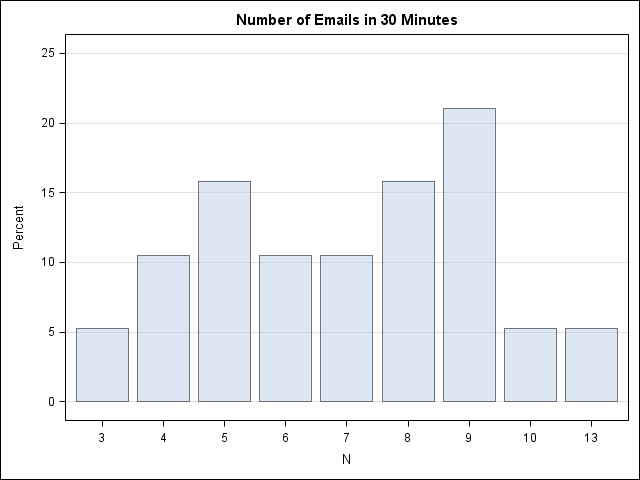
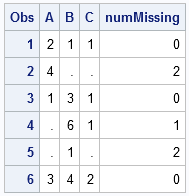
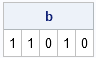
I blog about a lot of topics, but the following five categories represent some of my favorite subjects. Judging by the number of readers and comments, these articles have struck a chord with SAS users. If you haven't read them, check them out. (If you HAVE read them, some are