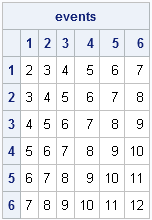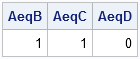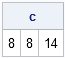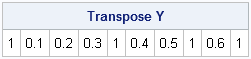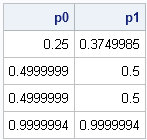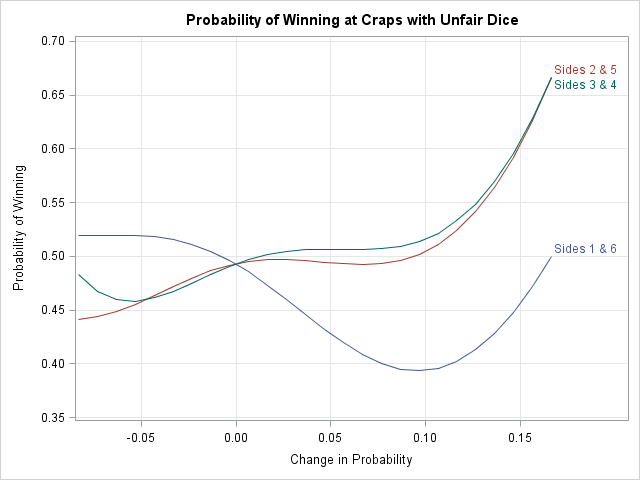
Last week I wrote a SAS/IML program that computes the odds of winning the game of craps. I noted that the program remains valid even if the dice are not fair. For convenience, here is a SAS/IML function that computes the probability of winning at craps, given the probability vector