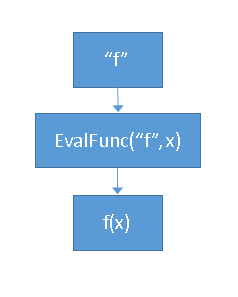
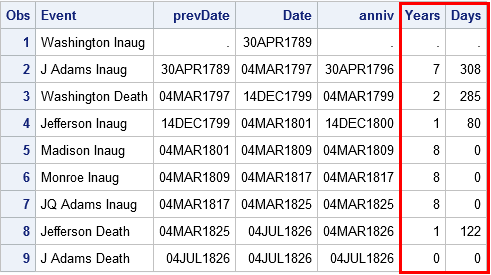
Have you ever seen the "Fit Summary" table from PROC LOESS, as shown to the right? Or maybe you've seen the "Model Information" table that is displayed by some SAS analytical procedures? These tables provide brief interesting facts about a statistical procedure, hence they are called factoids. In SAS, a