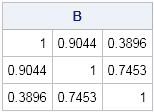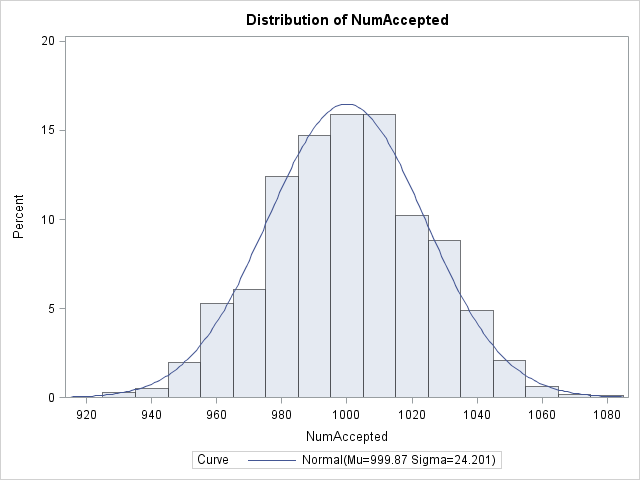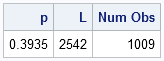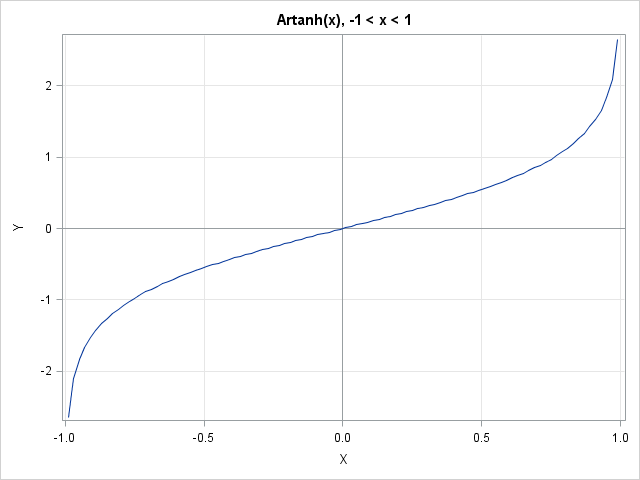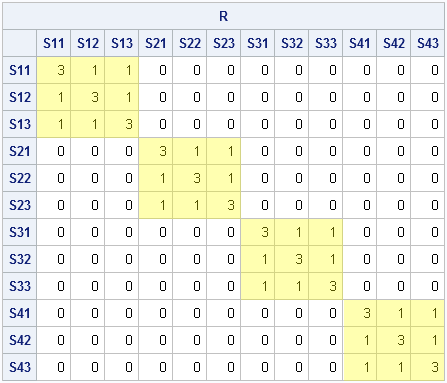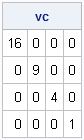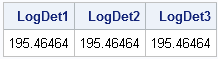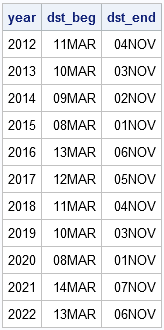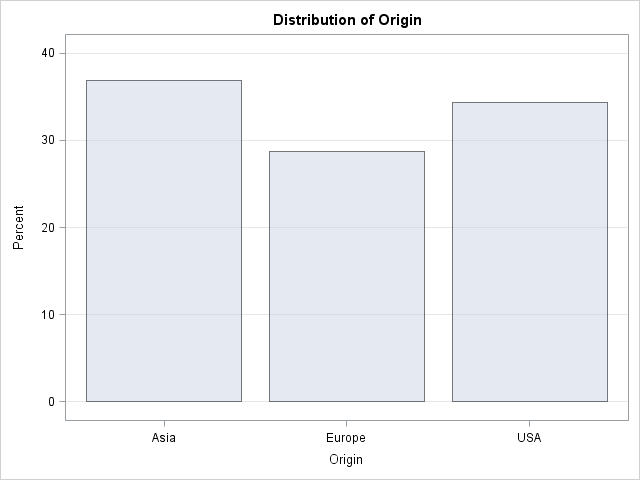
It seemed like an easy task. A SAS user asked me how to use the SGPLOT procedure to create a bar chart where the vertical axis shows percentages instead of counts. I assumed that there was some simple option that would change the scale of the vertical axis from counts