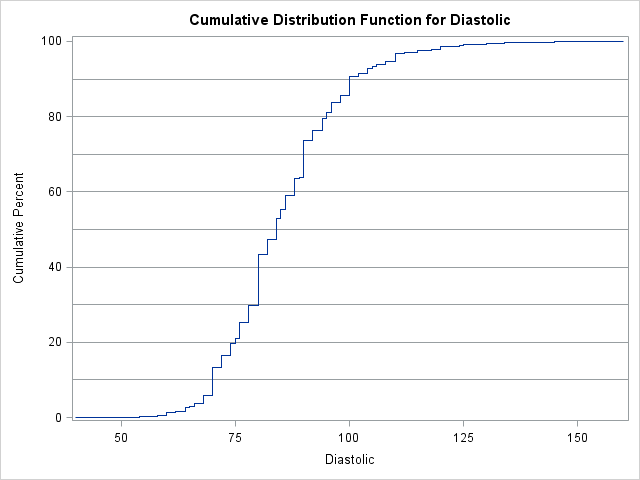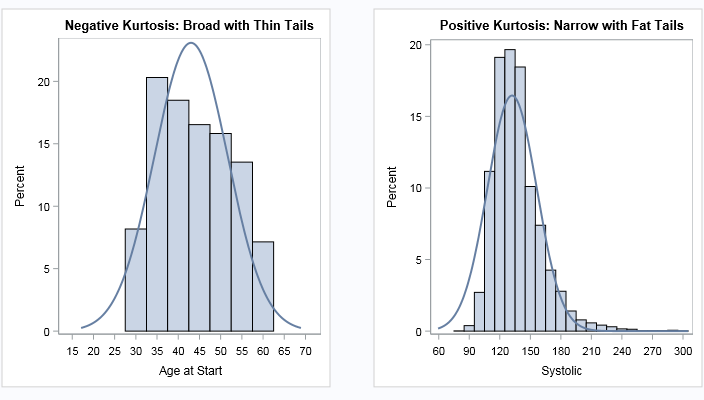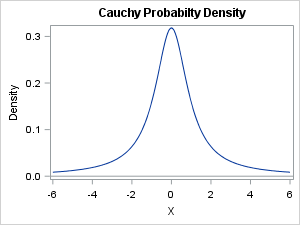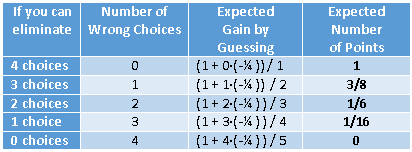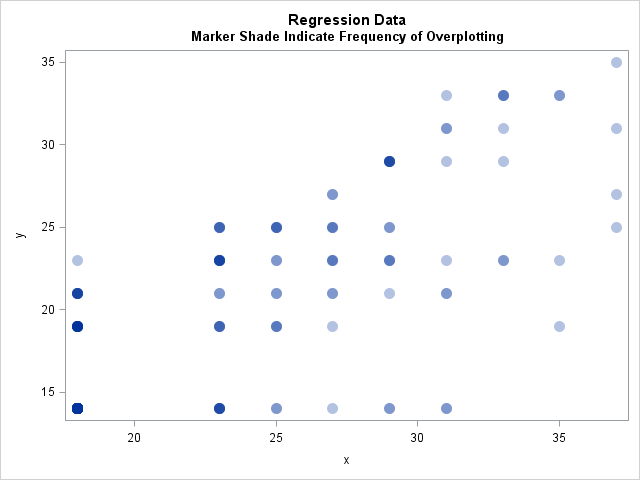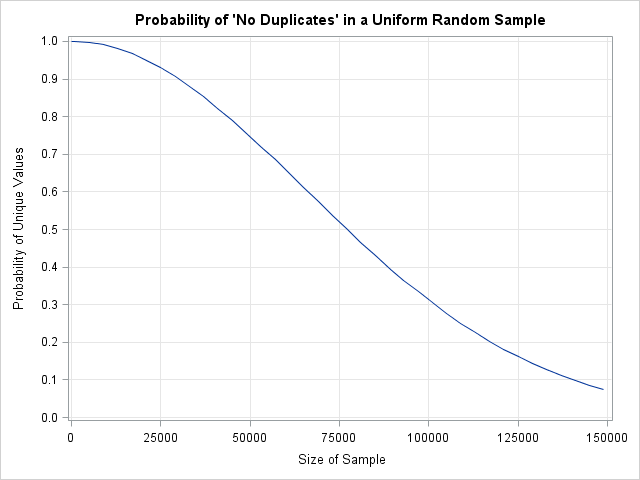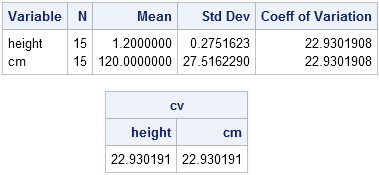
I sometimes wonder whether some functions and options in SAS software ever get used. Last week I was reviewing new features that were added to SAS/IML 13.1. One of the new functions is the CV function, which computes the sample coefficient of variation for data. Maybe it is just me,