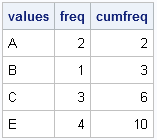
A reader asked: I want to create a vector as follows. Suppose there are two given vectors x=[A B C] and f=[1 2 3]. Here f indicates the frequency vector. I hope to generate a vector c=[A B B C C C]. I am trying to use the REPEAT function

A reader asked: I want to create a vector as follows. Suppose there are two given vectors x=[A B C] and f=[1 2 3]. Here f indicates the frequency vector. I hope to generate a vector c=[A B B C C C]. I am trying to use the REPEAT function
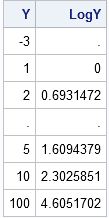
SAS software provides many run-time functions that you can call from your SAS/IML or DATA step programs. The SAS/IML language has several hundred built-in statistical functions, and Base SAS software contains hundreds more. However, it is common for statistical programmers to extend the run-time library to include special user-defined functions.
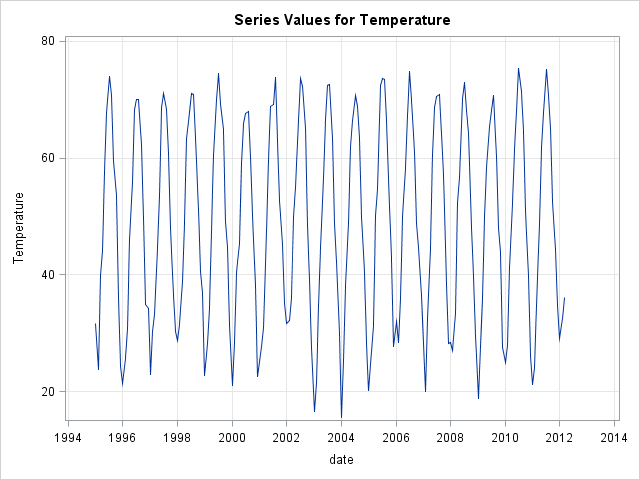
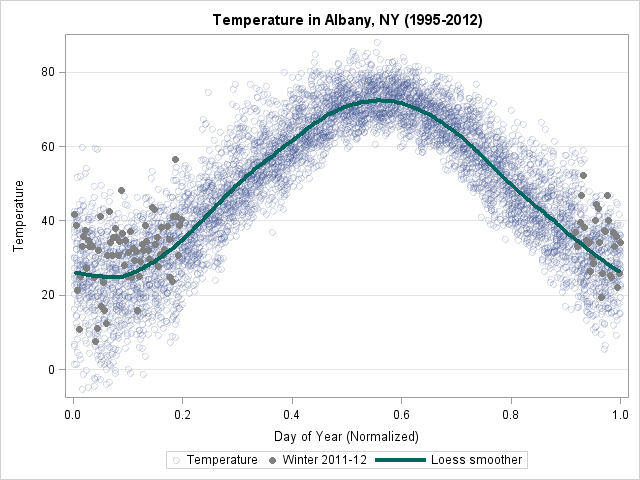
Last week I blogged about how to construct a smoother for a time series for the temperature in Albany, NY from 1995 to March, 2012. I smoothed the data by "folding" the time series into a single "year" that contains repeated measurements for each day of the year. Experts in
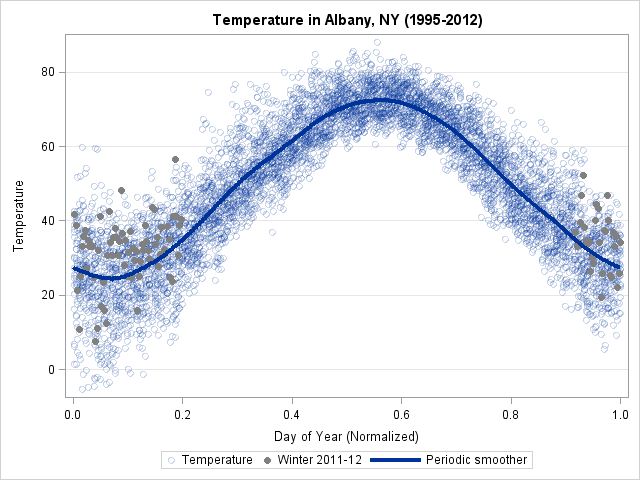
In yesterday's post, I discussed a "quick and dirty" method to smooth periodic data. However, after I smoothed the data I remarked that the smoother itself was not exactly periodic. At the end points of the periodic interval, the smoother did not have equal slopes and the method does not
Over at the SAS and R blog, Ken Kleinman discussed using polar coordinates to plot time series data for multiple years. The time series plot was reproduced in SAS by my colleague Robert Allison. The idea of plotting periodic data on a circle is not new. In fact it goes
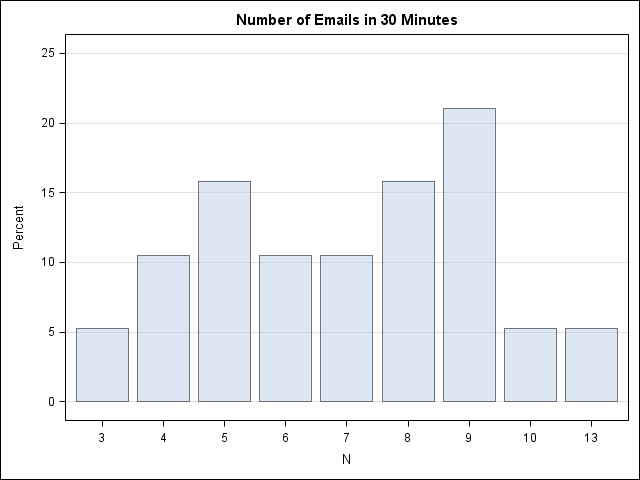
Over at the SAS Discussion Forums, someone asked how to use SAS to fit a Poisson distribution to data. The questioner asked how to fit the distribution but also how to overlay the fitted density on the data and to create a quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plot. The questioner mentioned that the
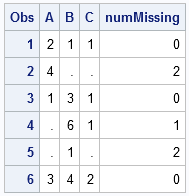
Locating missing values is important in statistical data analysis. I've previously written about how to count the number of missing values for each variable in a data set. In Base SAS, I showed how to use the MEANS or FREQ procedures to count missing values. In the SAS/IML language, I
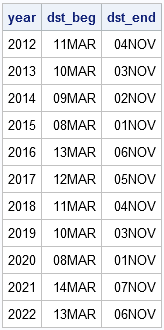
In the United States, this upcoming weekend is when we turn our clocks forward one hour as we adopt daylight saving time. (Some people will also flip their mattresses this weekend!) Daylight saving time (DST) in the US begins on the second Sunday in March and ends on the first

The SAS DATA step supports a special syntax for determining whether a value is contained in an interval: y = (-2 < x < 2); This expression creates an indicator variable with the value 1 if x is in the interval (-2,2) and 0 otherwise. There is not a standard
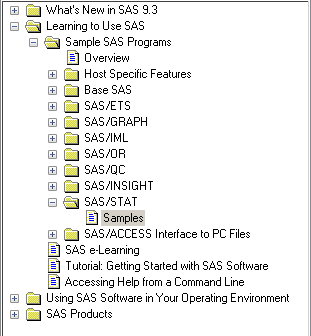
Have you ever wanted to run a sample program from the SAS documentation or wanted to use a data set that appears in the SAS documentation? You can: all programs and data sets in the documentation are distributed with SAS, you just have to know where to look! Sample data