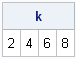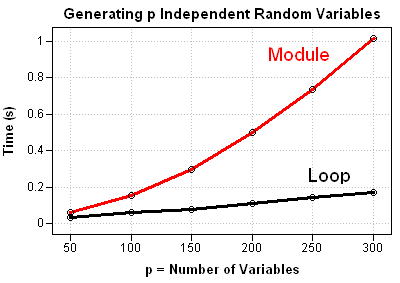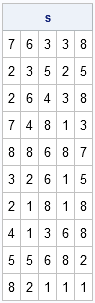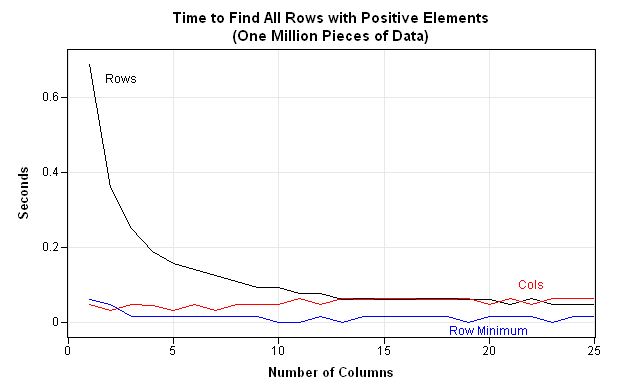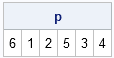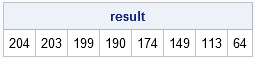
Recently Charlie Huang showed how to use the SAS/IML language to compute an exponentially weighted moving average of some financial data. In the commentary to his analysis, he said: I found that if a matrix or a vector is declared with specified size before the computation step, the program’s efficiency