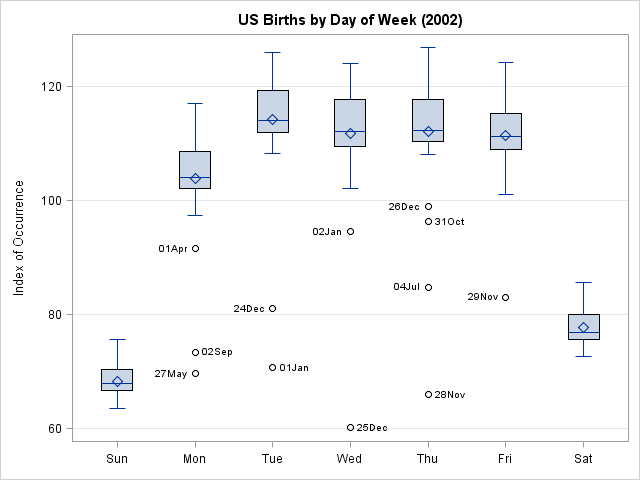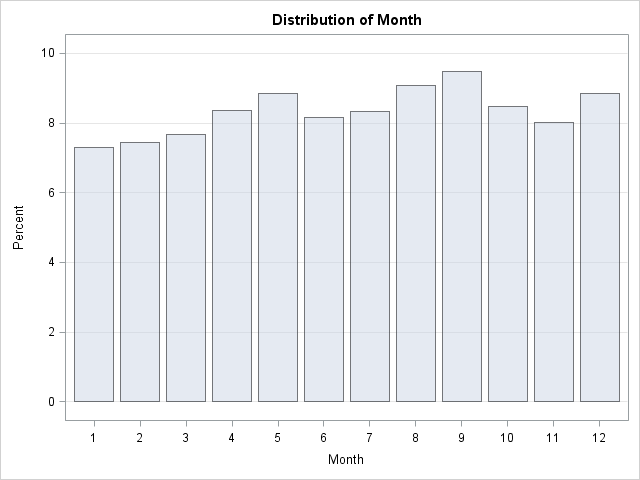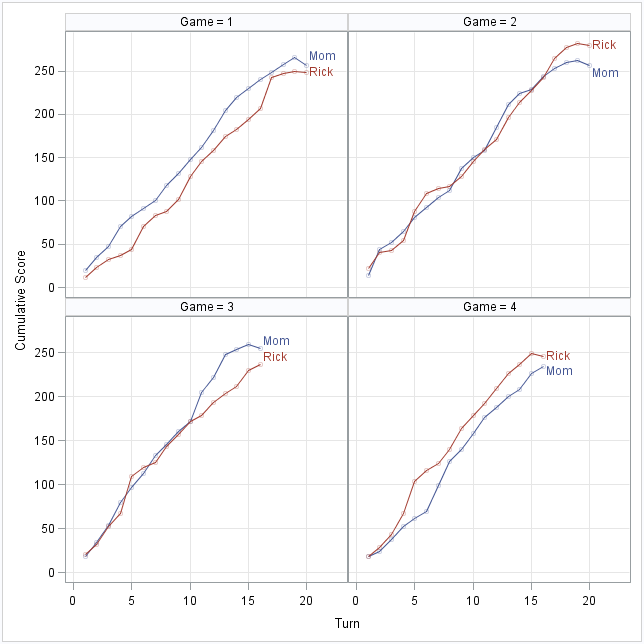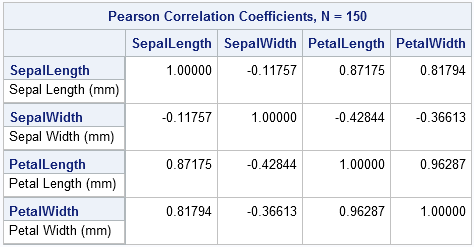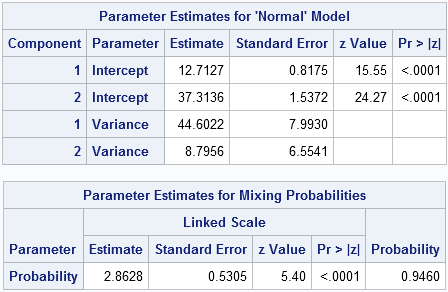
In my previous post, I blogged about how to sample from a finite mixture distribution. I showed how to simulate variables from populations that are composed of two or more subpopulations. Modeling a response variable as a mixture distribution is an active area of statistics, as judged by many talks