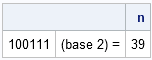
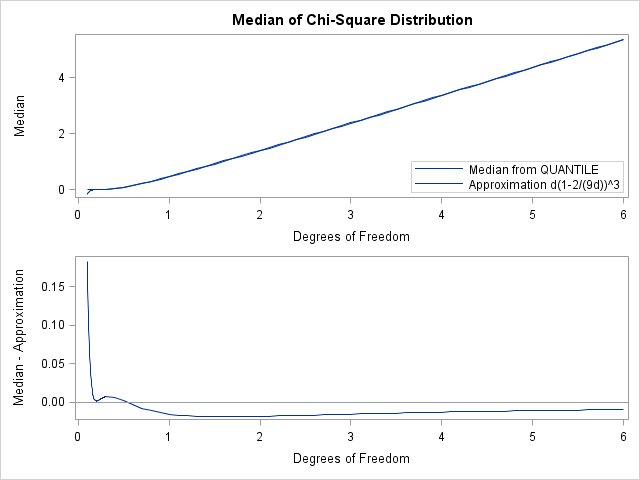
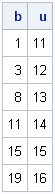
Here's a quick tip to keep in mind when you write SAS/IML programs: although the SAS/IML documentation lists about 300 functions that are built into the SAS/IML language, you can also call hundreds of functions in Base SAS. Furthermore, you can pass in SAS/IML vectors for arguments to the functions.