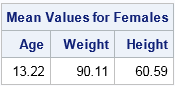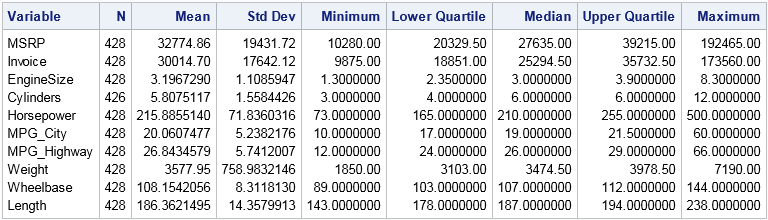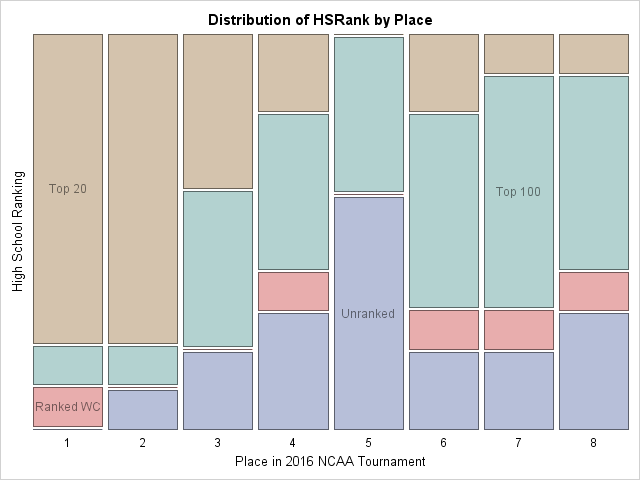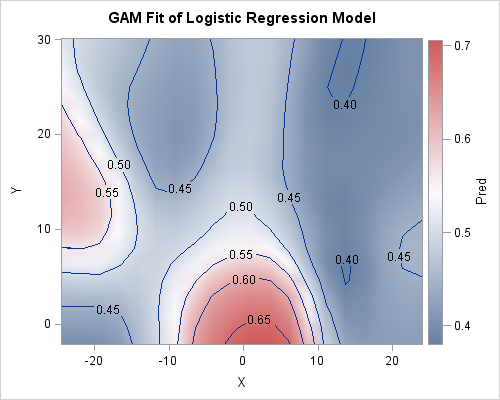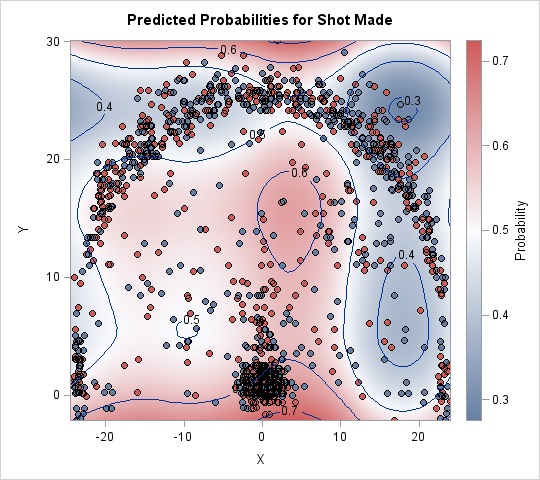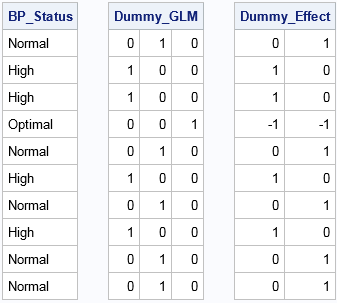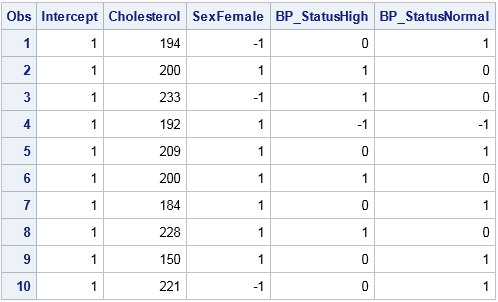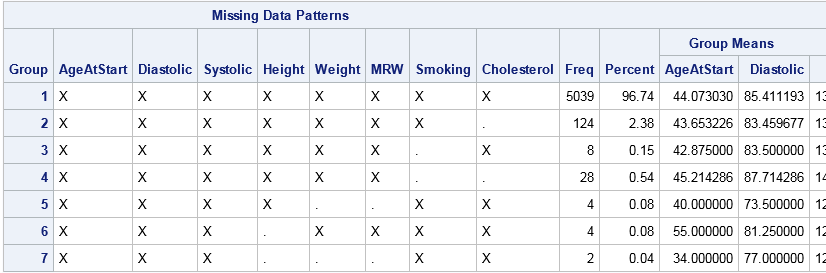
Missing data can be informative. Sometimes missing values in one variable are related to missing values in another variable. Other times missing values in one variable are independent of missing values in other variables. As part of the exploratory phase of data analysis, you should investigate whether there are patterns