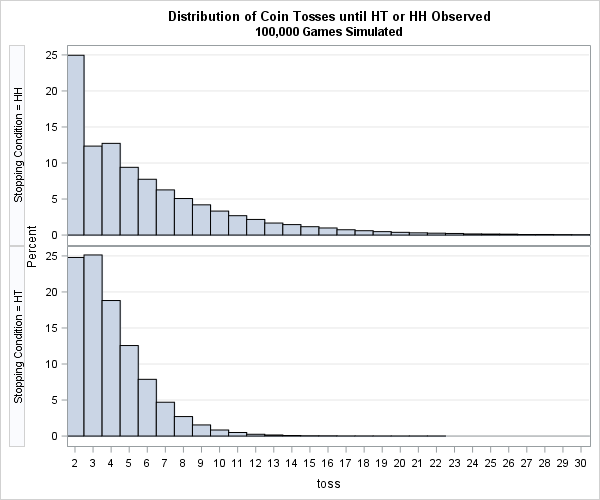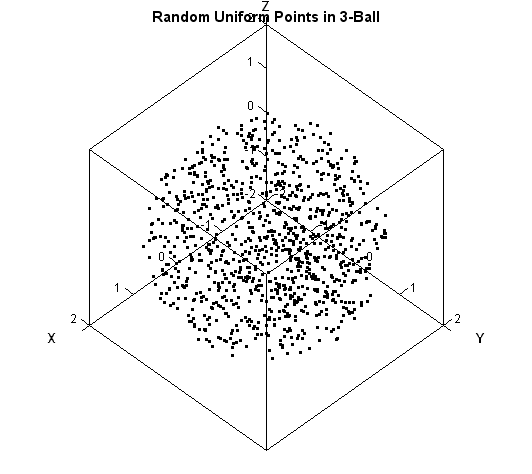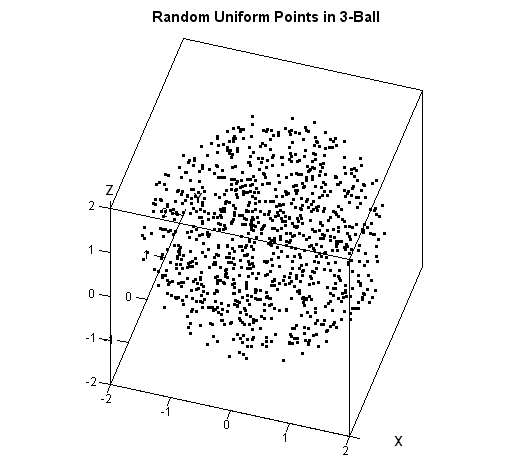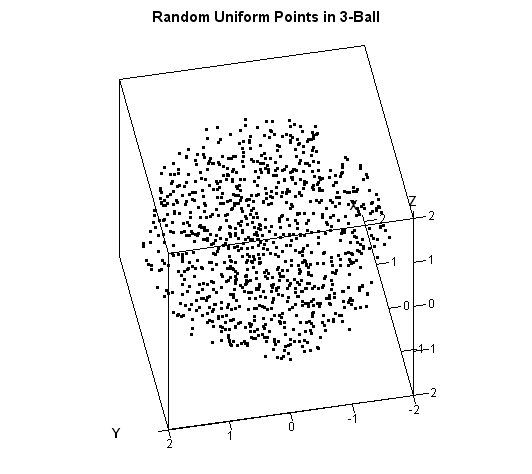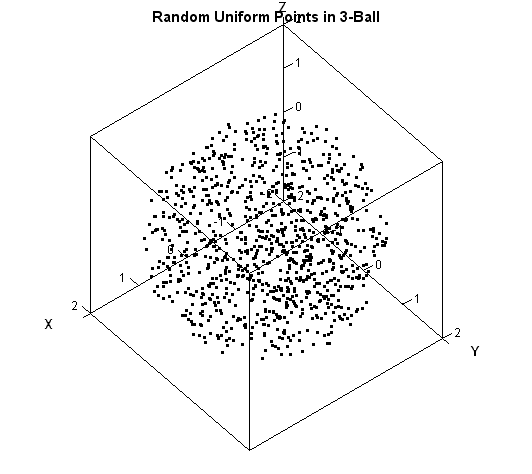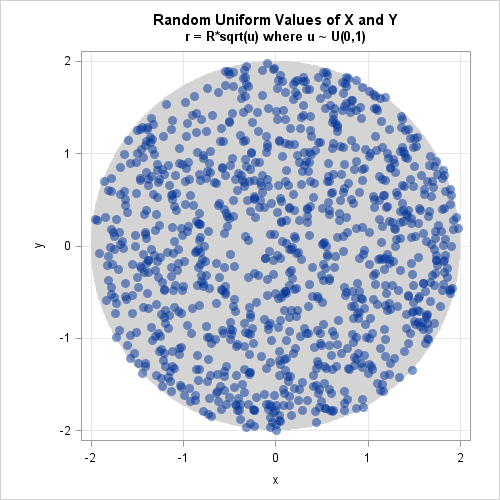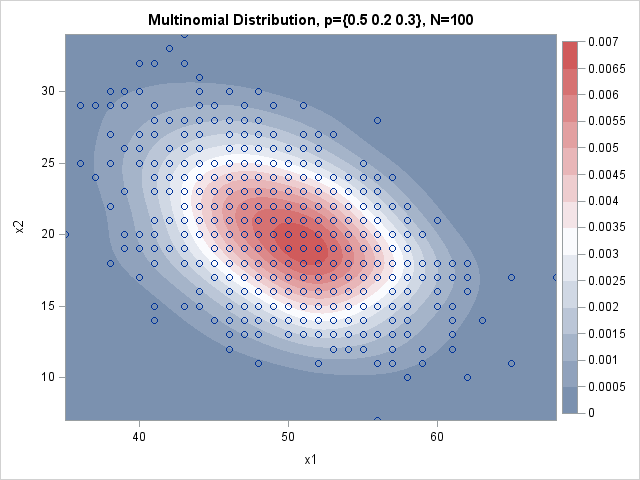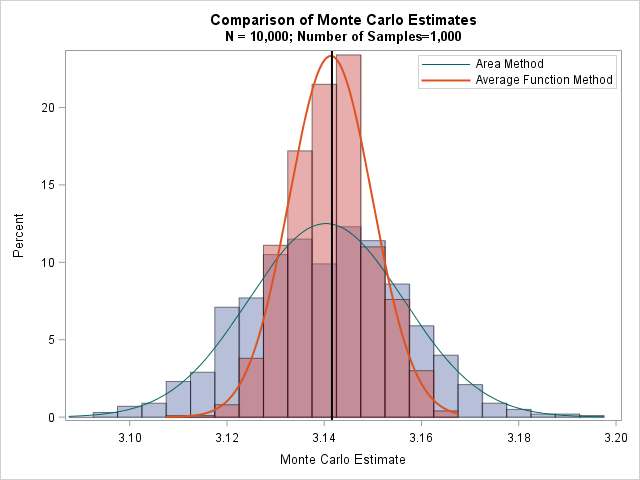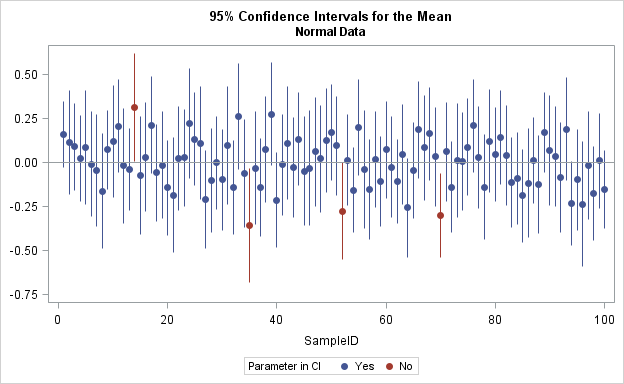
The article uses the SAS DATA step and Base SAS procedures to estimate the coverage probability of the confidence interval for the mean of normally distributed data. This discussion is based on Section 5.2 (p. 74–77) of Simulating Data with SAS. What is a confidence interval? Recall that a confidence