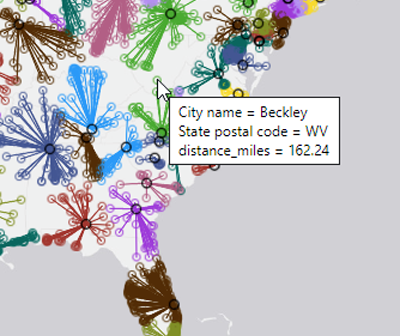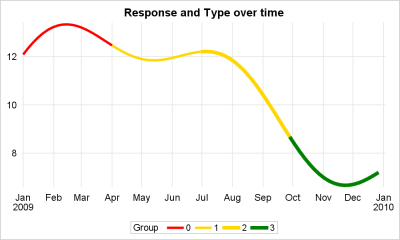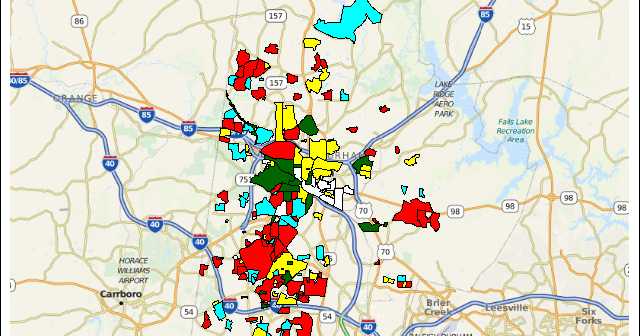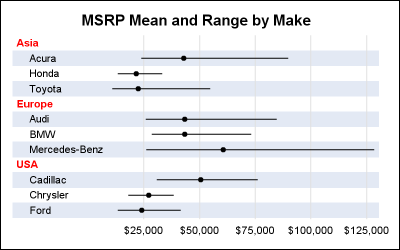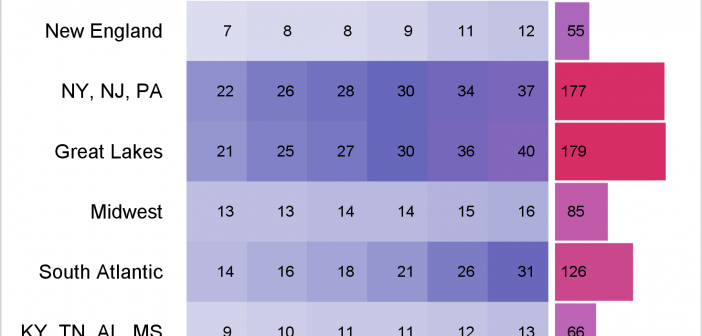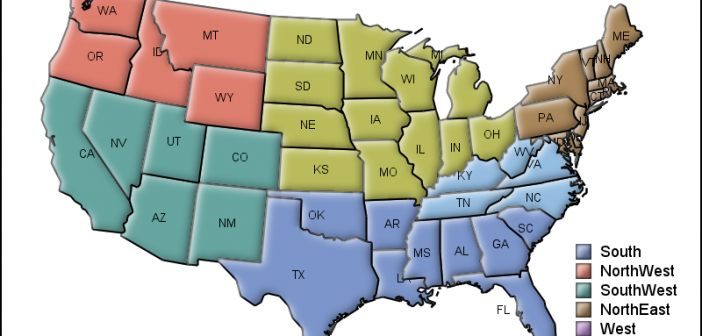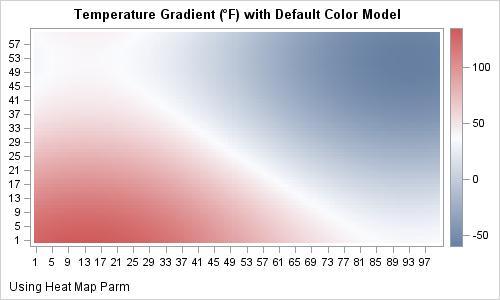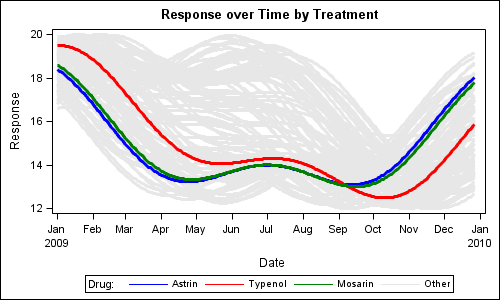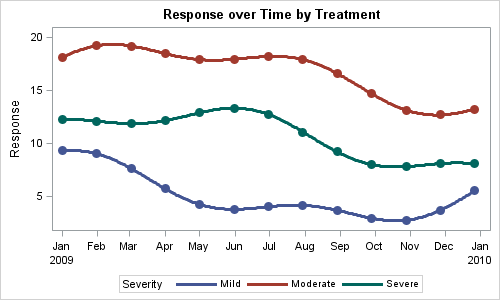
When you get something new, the hope is that it will be better than the old thing it's replacing. As I often do, I asked my Facebook friends to provide a random picture for my blog - in this case, a picture of one of their new/recent purchases. My friend